Tea is steeped in tradition, for sure, but innovation is not forbidden. In Tanzania, Bente, who had the audacity to plant tea trees on a coffee plantation, cultivates a taste for creativity. Sometimes she hollows out papayas and fills them with tea so that the camellia leaves take on their aroma when they come into contact with the fruit. At other times, she blows hot air onto sliced bananas, infusing the tea with a new fragrance. And she does everything in the most artisanal way possible. Bravo Bente!
Tea processing
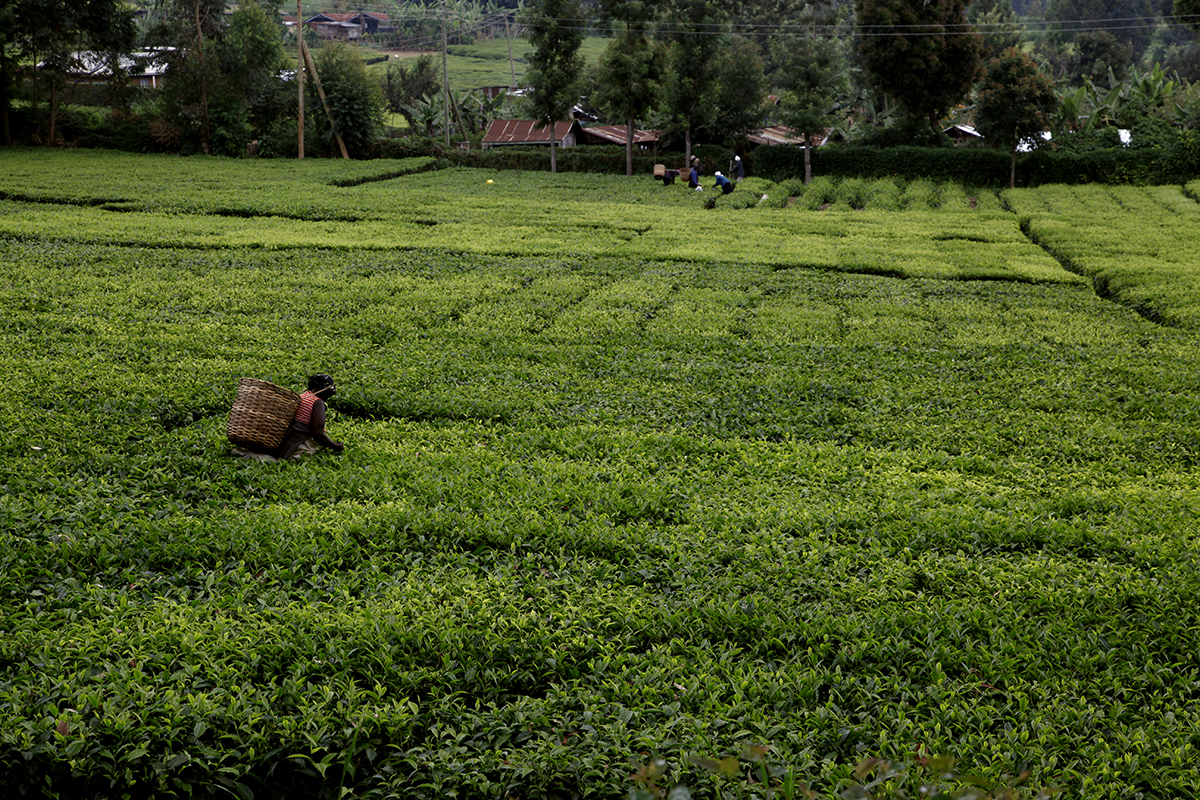
Roll out the green carpet
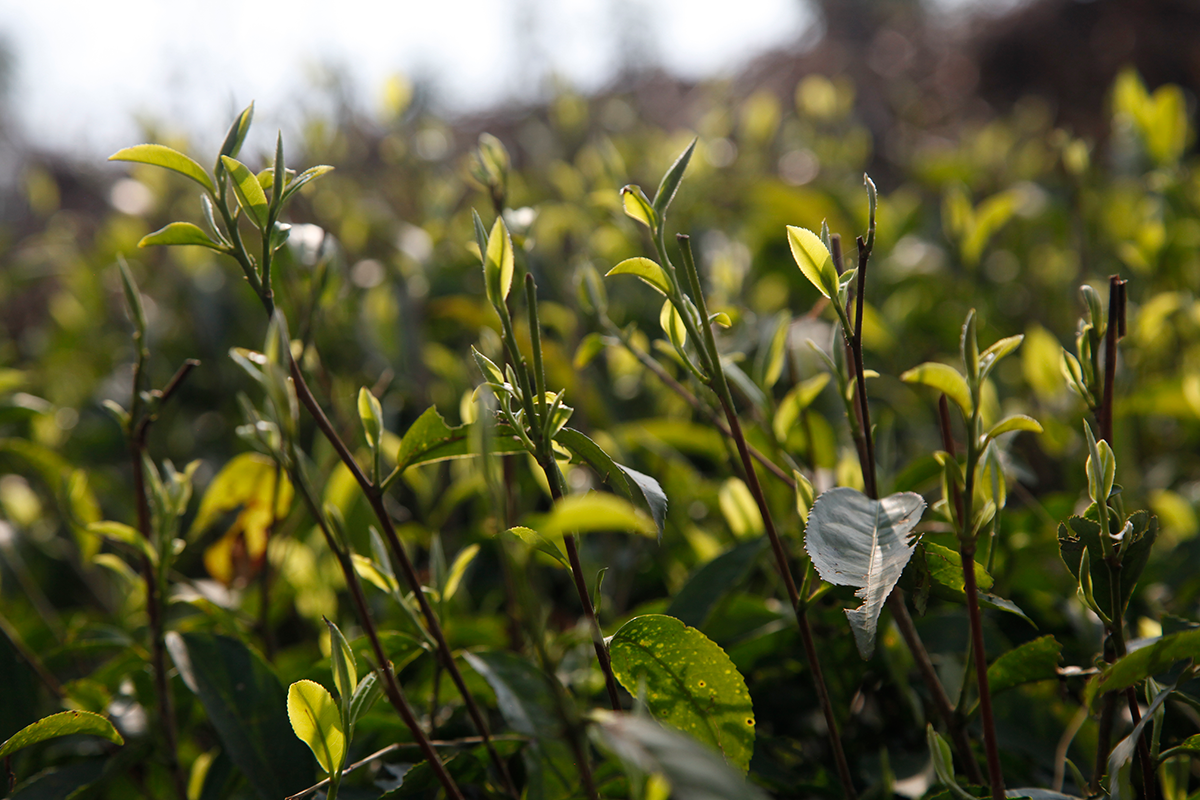
It takes a lot of attention to detail to produce fine tea, harvested from this beautiful emerald expanse. Only the bud and the first two youngest leaves at the tip of the shoot must be picked. The subsequent stages in production also play an important role in quality. Let’s roll out the green carpet for everyone who helps to create such delicious teas.
Alex cultivates curiosity
By the time you read this, I’ll be with my friend Alex, tasting each of his teas. His Satemwa plantation in Malawi is one of the best in Africa. Not content with making tea for industrial producers, Alex set up different workshops to enable him to experiment – with success. He’s tried all types of processing methods to make semi-oxidised, green, white, fermented, smoked and sculpted teas. Curiosity doesn’t kill the cat; on the contrary, it helps us progress, and Alex is a brilliant example.
SafeTea™, our safety system
Two weeks ago I promised you that a wonderful Rohini Early Spring would be arriving, and that it would be available after the obligatory food safety analyses. Sadly, we must wait a little longer. At Palais des Thés we follow our own special procedure, called SafeTea™, which guarantees that our teas meet the optimal food safety standards. We carry out random tests on our organically certified teas (AB label). For all other teas we sell, we ensure they comply with our standards by having them analysed by an independent laboratory. Our checks go beyond the legal requirements. But this does mean we have to wait a few days longer while the tests are being carried out, to ensure the safety of our teas.
Something for every taste
Attitudes are changing and this makes me happy. In the early days of Palais des Thés, Chinese teas really divided our customers. Some loved them, others hated them based on the premise that all Chinese teas were smoked to a greater or lesser extent. There was a lot of misunderstanding surrounding them. Thirty years later, it’s such a pleasure to see how things have changed. Not only do many people now realise that not all Chinese teas are smoked, but we have also seen the rise in popularity of green, white, blue-green, yellow, dark and black teas from this country, the birthplace of tea.
Papayas and tea
People are always experimenting, and when you’re lucky enough to be a tea researcher, you’re well placed to see all sorts of things. Here, on a coffee plantation in Tanzania that has branched out into growing tea, there is no lack of innovation. The latest initiative is to remove the flesh of papayas and fill the skins with a semi-oxidised tea that has been withered and rolled. After a short oxidation, the wet leaves are stuffed into the hollowed-out ripe fruit and become impregnated with its delicious scent.
Isolation and fermentation
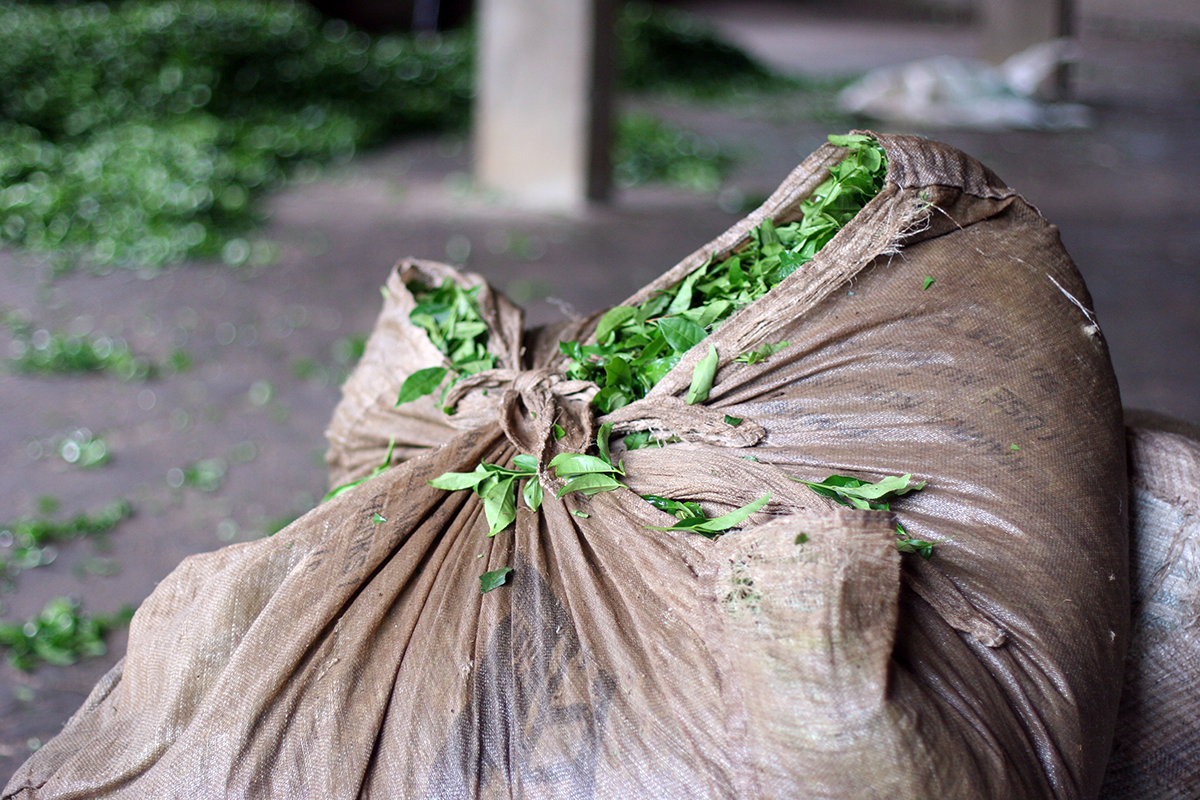
Freshly plucked tea leaves shouldn’t be kept in isolation, or they might start to ferment. As soon as they are harvested they are transported to the factory in bags made from a light, loosely woven material that allows air to circulate. The journey must be as short as possible to prevent the risk of the young shoots undergoing an undesirable change.
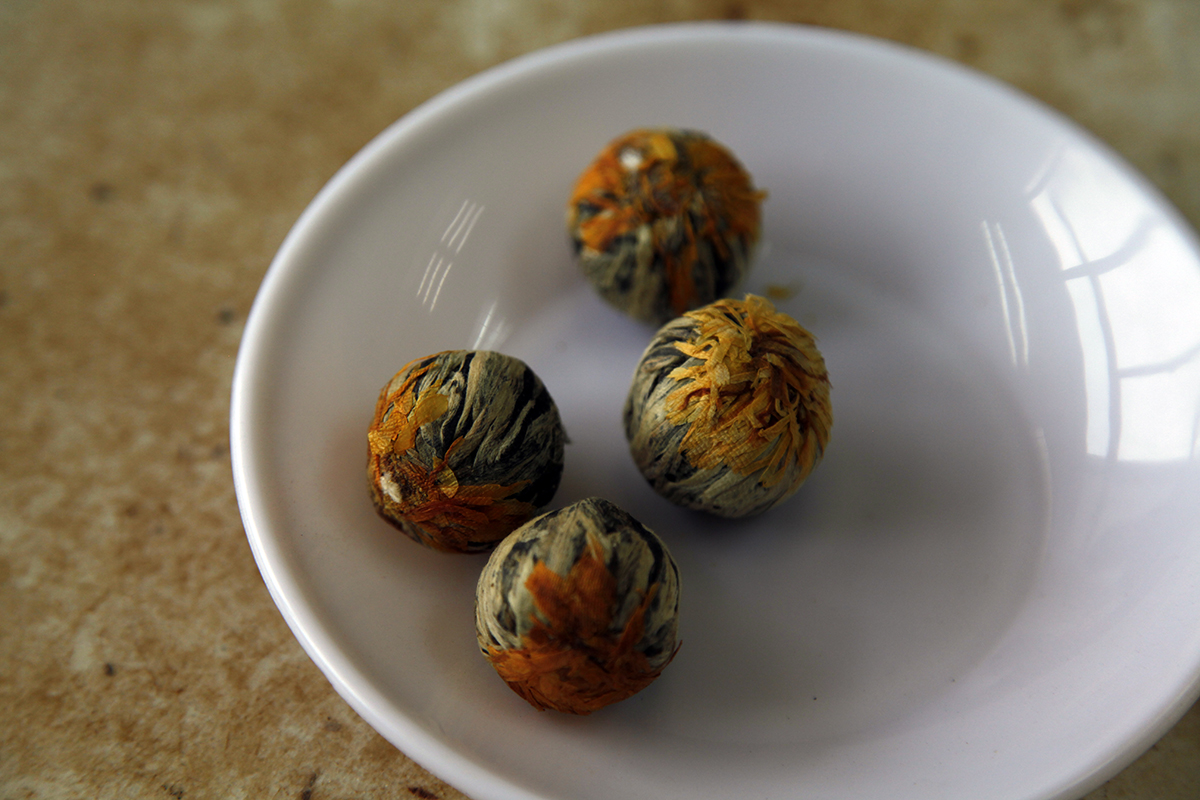
Balls of tea
There are endless ways to shape tea, or compress it. Tea leaves can be shaped into needles, pearls, sticks, twists, old man’s eyebrows, birds’ tongues, melon seeds – there are many evocative descriptions in Chinese terminology.
Tea can also be compressed. This is mainly done with dark teas, but sometimes with white teas and certain black teas too. They become bricks, cakes or, as you can see here, simple balls.
Teas shelter in place to develop powerful aromas
If there is one type of tea that could be described as being in “confinement”, which is our term for “lockdown” or “shelter in place” here in France, it is shade-grown teas. The best known of these is Pu Erh.
These teas generally go into confinement by being shaded for one to two months, although it can be longer. And when it comes to “deconfinement”, when you lift off the covers under which the harvested leaves have been gently fermenting, you are greeted with wonderful, powerful bouquets. In the cup, these teas develop magnificent aromas of undergrowth, cellars, mushrooms, sought-after animal notes that often evoke stables, and spices. Here’s to your “deconfinement”, whenever that may be.
The joy of singing
They haven’t seen one for nearly twenty years – a rainy winter. For almost two decades, planters constantly complained about the dryness in January or February, or both. In 2017 the weather really was against them: not a single drop of rain fell between October and March. At last, in 2020, the region was treated to magnificent rainfall all winter. But water isn’t everything. For the leaves to grow, they need heat too. And this year, it’s too cold for them.
While we wait for the soil to warm up, we’re tasting last year’s teas again, to remind ourselves of them, as well as the few low-altitude batches that have been freshly produced in miniscule quantities. Meanwhile, the pickers keep themselves happy by singing.