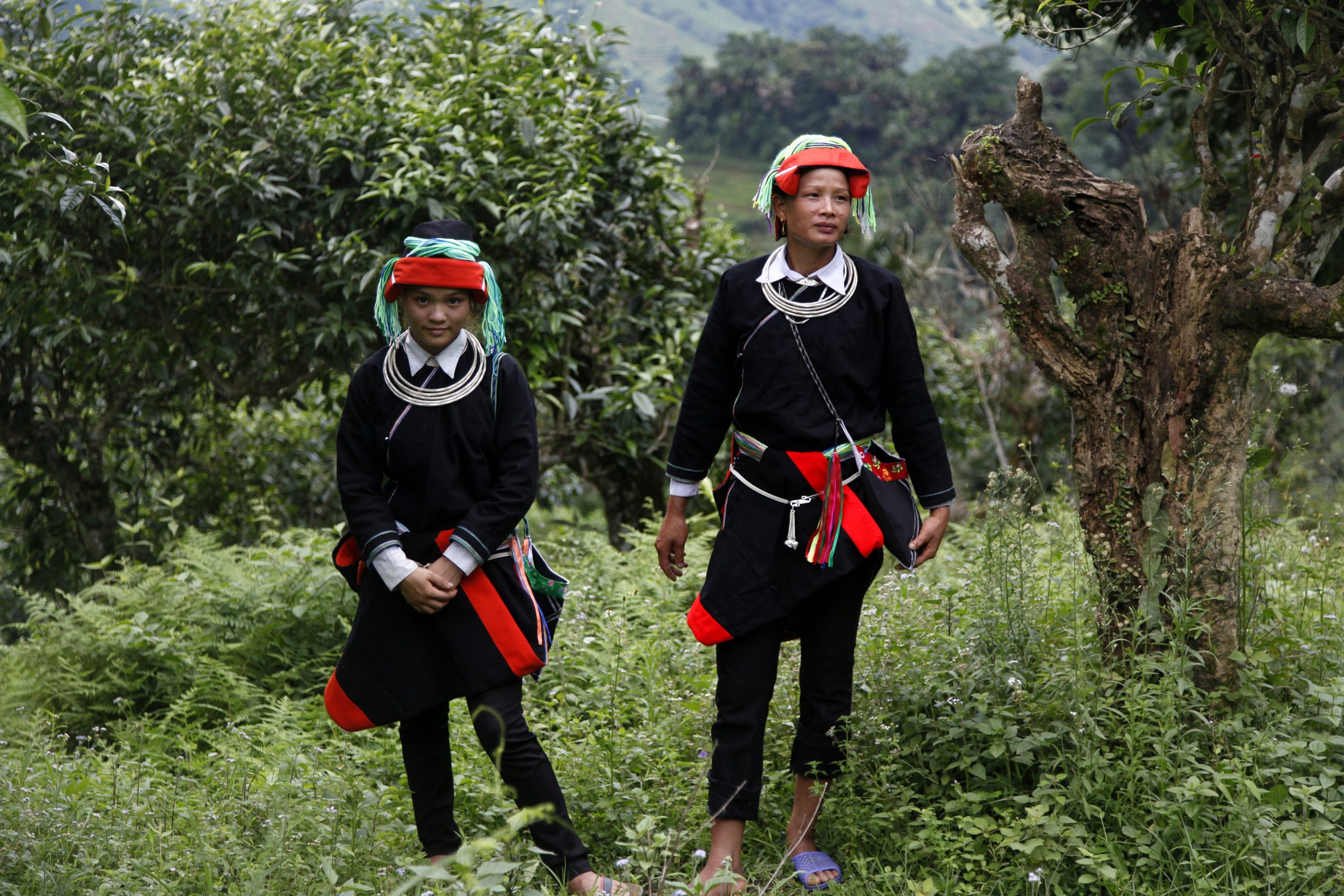
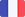
When people ask me which trips have left the greatest impression on me, I naturally think of the breathtaking landscapes, the Himalayan foothills, the active volcanoes rising up behind the tea fields. I remember the beautiful Japanese tea gardens, the multi-hued trees of Sri Lanka standing in a sea of Camellia sinensis. I recall the long train journeys through all kinds of jungle, and all the times I’ve sat down on a mountain road just to contemplate the beauty of the world. But the experiences that have marked me the most are the human encounters. They are in essence all unique and so many memories come to mind. Among them, the tea pickers of the Golden Triangle from one or other of the region’s ethnic groups (shown here, two Dao women), who we would come across at random in a tea garden hidden deep in a remote forest, after hours of walking.
Vietnam
A wet shirt
Lotus tea is a Vietnamese tradition. To grow the flowers, you have to get wet. You get wet when it’s time to harvest the flowers. You get wet in the pond, either wading through the chest-height water or in the little leaky boats. And you get wet when it’s time to divide up Nelumbo nucifera by plunging your hand down towards the bottom and grabbing a few rhizomes, which will be planted out in another pond.
Lotus tea: a Vietnamese tradition
The lotus flower plays a very important role in Vietnamese culture. So it’s not surprising that the country has a tradition of flavouring tea with the flower, resulting in a particularly sought-after beverage. Production takes place in June and July and requires patience, as the tea leaves are left in contact with the flower pollen for five days in a row.
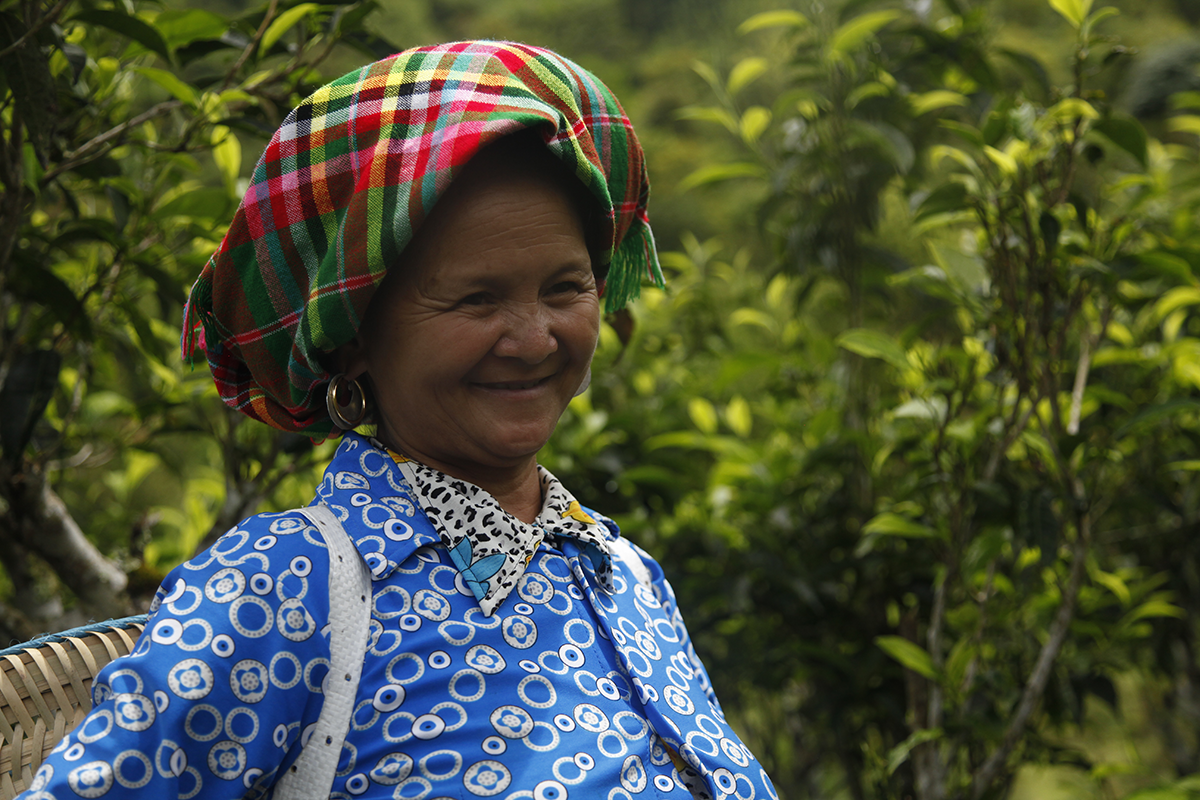
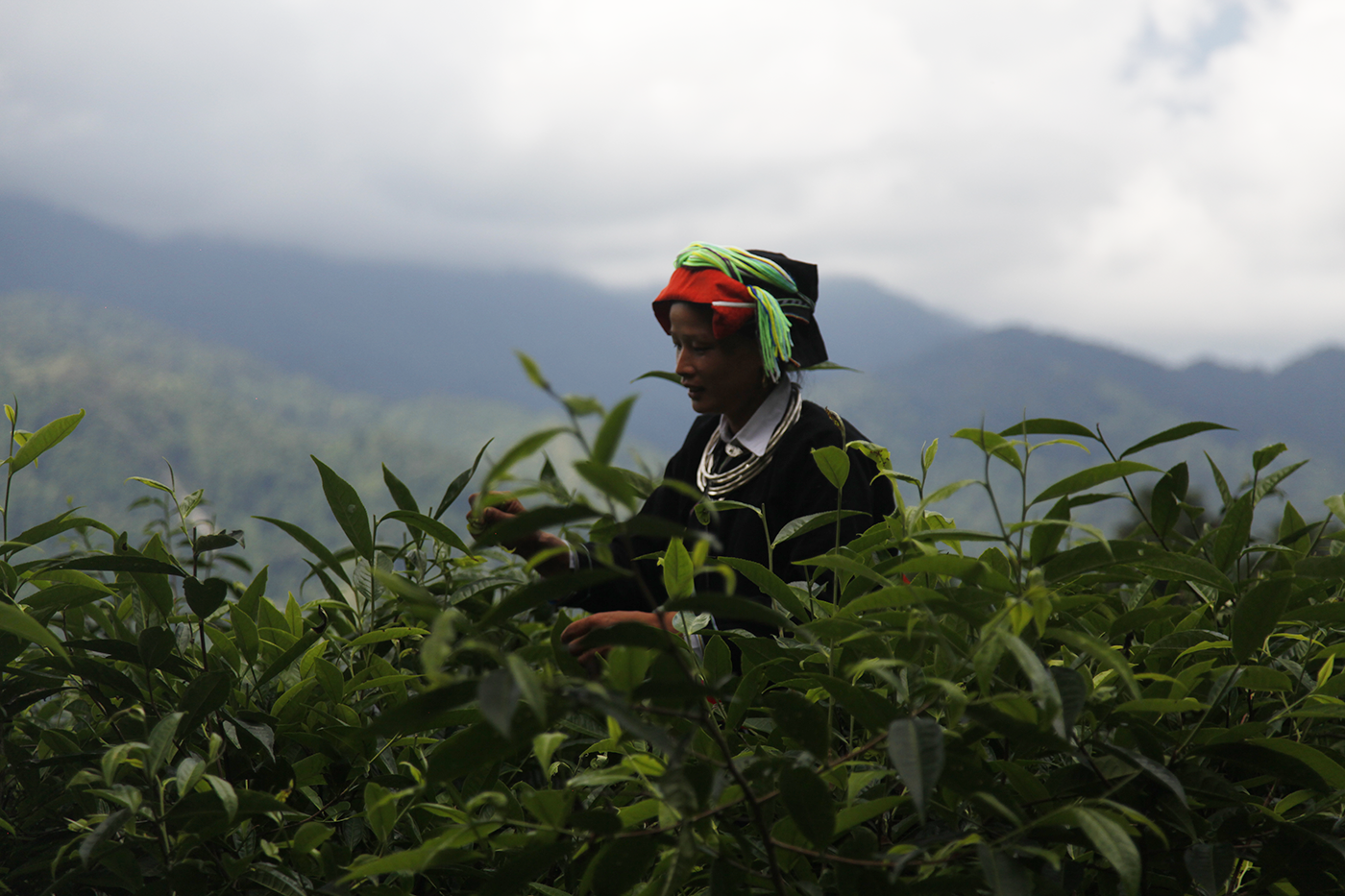
A Hmong woman
The Golden Triangle is a fascinating region thanks to its varied geography, mountains covered in jungle, hidden valleys and, most of all, the many and varied ethnic groups who have made it their home. Each ethnic group has its own culture, language and customs. From one to another, the styles of houses change, their relationship with the land changes, the food changes. Here in Sung Do, in northern Vietnam, a woman sets out to pick tea leaves from hundred-year-old trees.
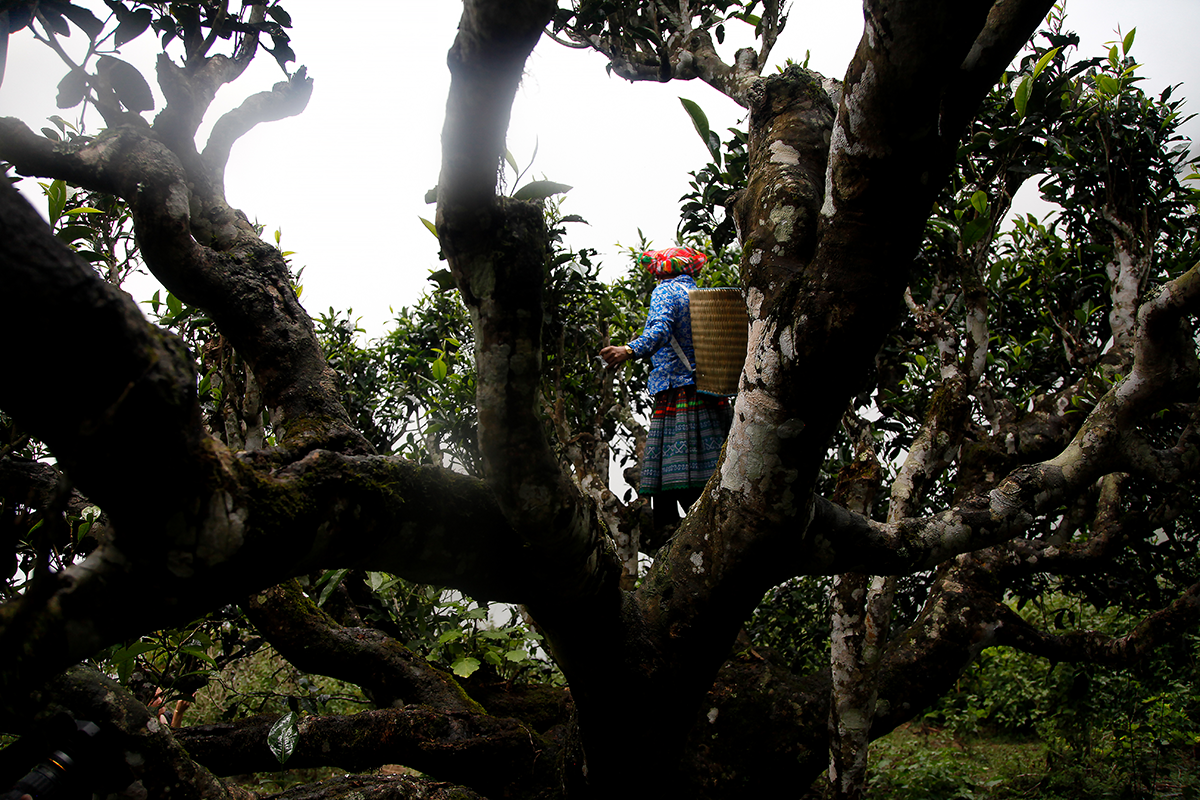
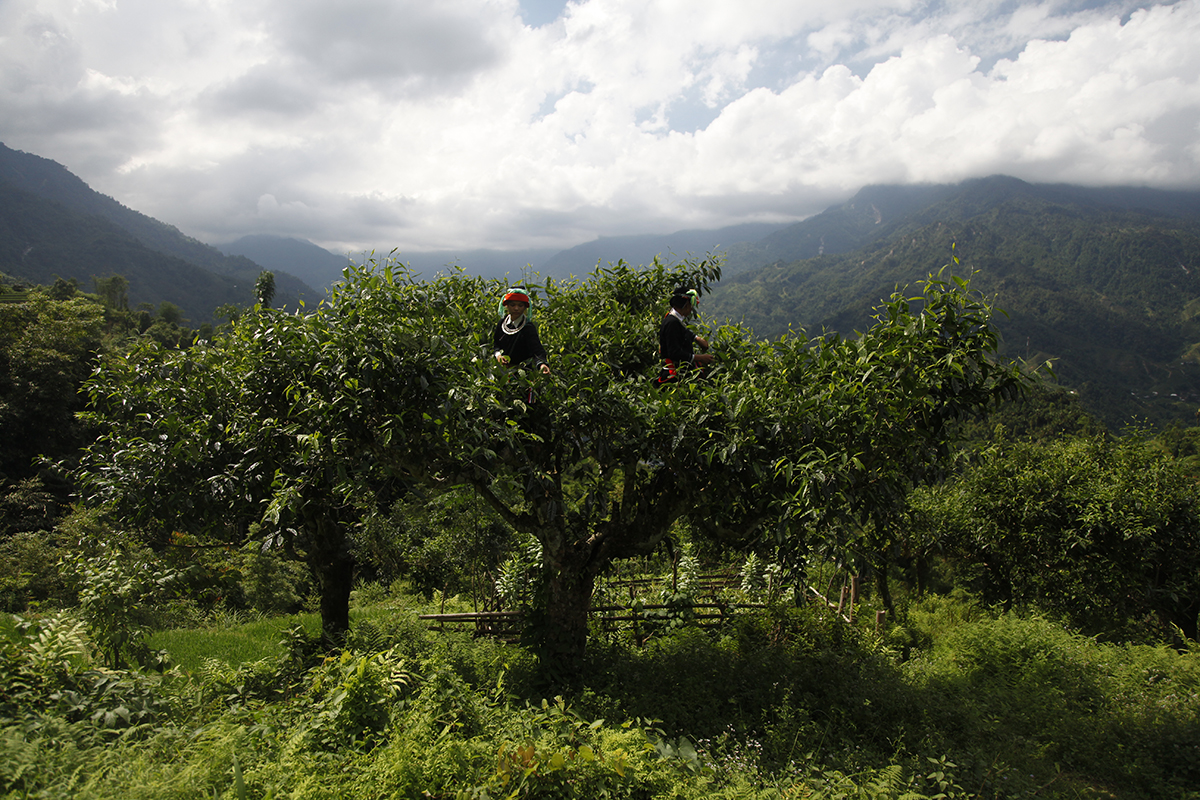
Harvesting in the treetops in the Golden Triangle!
In the region known as the Golden Triangle, you can find tea plants that are not quite like the others. Instead of being pruned at a low level to make it easier to pick the leaves, they are left to grow like trees. When harvest time comes, the pickers must climb up into the camellias, some of which are several hundred years old. The leaves from these trees are particularly sought-after to make Pu Erhs and dark teas.
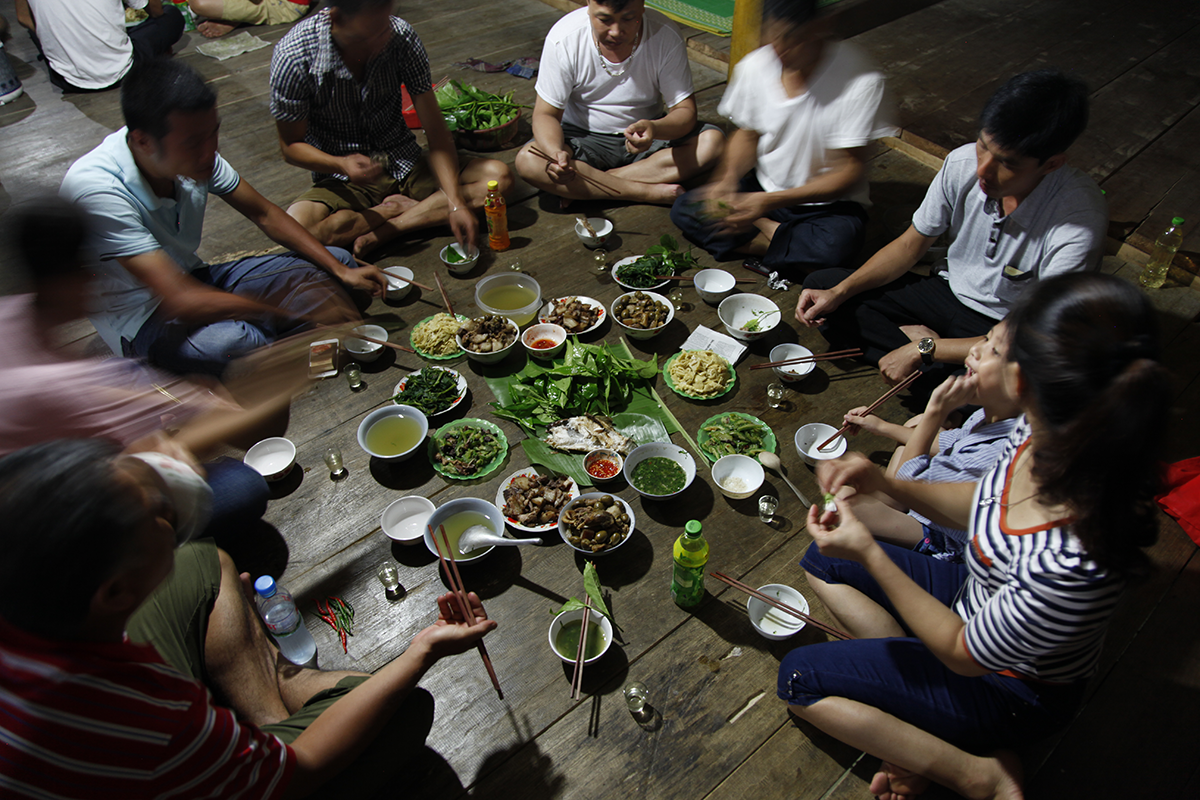
Following tradition
After a tiring day of walking for more than six hours to reach the old tea plants and then returning to the village, I needed to recover. The food in this region of northern Vietnam is delicious. With the Dao people who were hosting me, I followed tradition: throughout the meal, I toasted many times with the people who raised their glass to me. Each time I had to down my drink in one, and shake hands with them. Between slugs of the local rice alcohol, I took time to appreciate every tasty dish. The meals were prepared in the room where we sat to eat, on the ground. As soon as the meal was over we lay down on mats, in the same room, with nothing to separate us apart from a mosquito net between each person, not even from the jungle outside, with all its noises that interrupted my sleep. I could hear noises from the other mats: a mother breastfeeding her baby, someone else snoring loudly, another person coughing, and other various sighs and mutterings. By the time the cock crowed I’d been awake for some time, and I went outside to walk, to watch the day break from the edge of a rice field above the village. When I returned for breakfast and sat down, I was surprised to see the master of the house offer me more rice alcohol, and enthusiastically raise his glass in my direction. I declined. I couldn’t believe it, I was dreaming of tea, but in vain; my host was serious. He grew gloomy at my protestations, and would have been offended if I’d continued. Travelling is all about adopting the traditions of the people who are kind enough to welcome us, so I swallowed my drink. Later, he offered me a well-deserved tea, a tea I’d rarely longed for so much.
A mountain-top harvest
It’s not easy to reach the wild tea plants growing on the border between China and Vietnam, especially in the hot season. The stifling, muggy air slows you down, and the leeches that infest the region take advantage and cling on. You walk beneath a high sun. The humidity in the air is palpable. But once you’re out of the jungle, after a good three hours of walking, you find yourself high up, among the famous tea plants that have been left to grow like trees. You can enjoy this beautiful sight, especially if you’re lucky enough to arrive as the leaves are being picked. (To be continued.)
A mosaic of cultures
In regions where tea is picked from plants growing in the wild, whether that’s in southern Yunnan (China), northern Laos or here, in Vietnam, the villages are mainly populated by ethnic minorities. There is a great diversity of these minorities. Each one has its own customs, and sometimes its own language. When you walk through the mountains in these regions, you get to experience this mosaic of cultures. This woman, who is busy picking tea leaves from the top of a tree, belongs to the Dao community. (To be continued.)
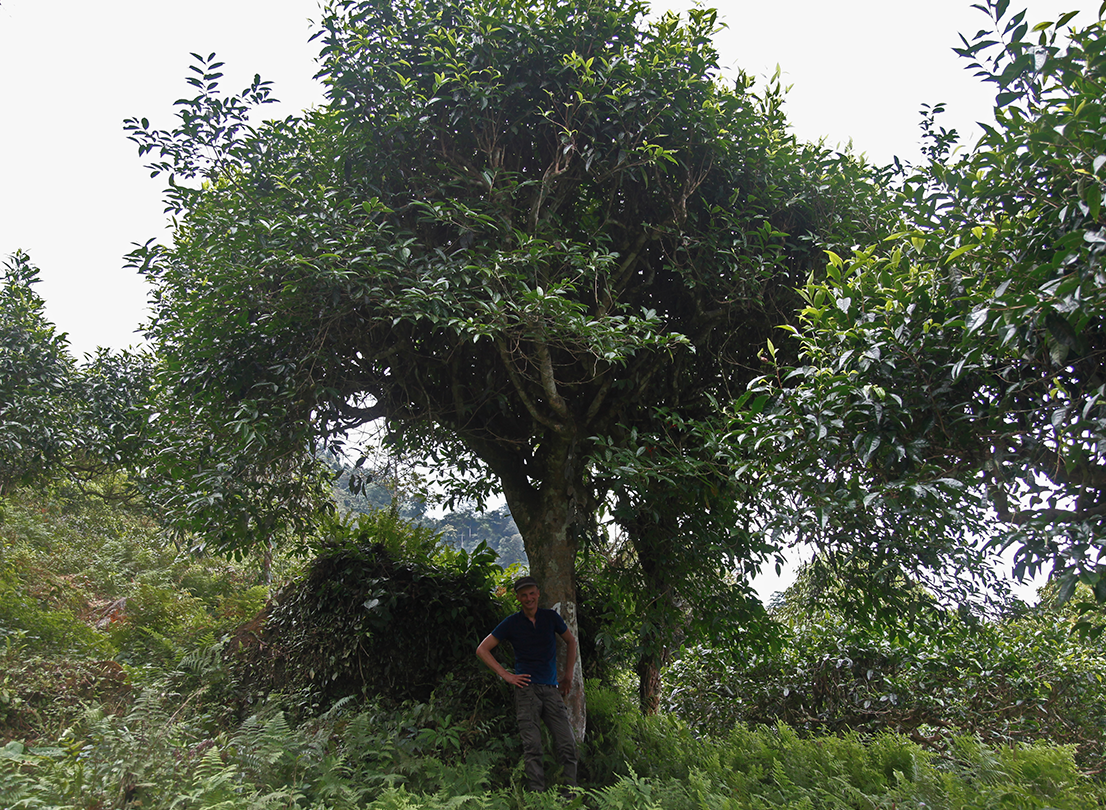
300 years old and it still has all its leaves
Here’s what a tea plant looks like when it has been left to grow, rather than being kept low so that its buds and shoots can be picked easily. From what I’ve been told in this far-flung corner of Vietnam, this camellia could be about 300 years old. I’m no expert in dating trees, but what I do know is that some very good teas are made using leaves harvested from these tea plants… (to be continued).
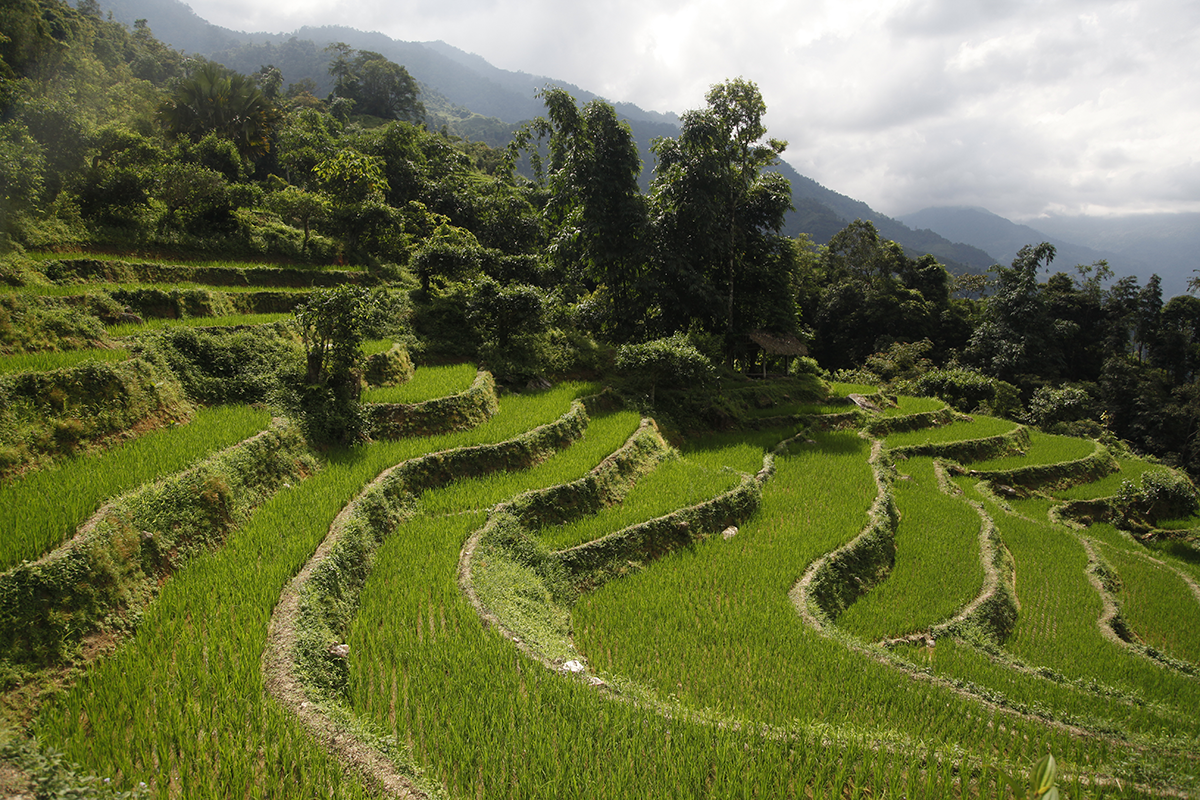
Tea and rice
Tea and rice have a lot in common. Firstly their shades of green, with the occasional touch of yellow, so delicate and varied, so intense. A feast for the eyes. I could spend my life photographing paddy fields. I often walk around them, carefully, placing one foot in front of the other along the low wall that surrounds them, in order to reach tea plantations that are even higher up the mountain, like here, in northern Vietnam. Some tea gardens have no road leading to them, so you set out on the sinuous path of the paddy fields. At least here it’s not steep, because rice grows on flat ground, either in fields or on terraces. Rice, unlike tea, needs stagnant water. Tea needs plenty of water too, but the water must be free-flowing, not sitting around its roots. That’s why tea likes slopes, while rice likes flat land. Flat versus slope, valley versus mountain, stagnant water versus flowing water; tea and rice are like two brothers who are completely opposite yet inseparable. They’re always together. They have another important human characteristic: of all agricultural products, these two crops employ the greatest number of people in the world. (To be continued.)