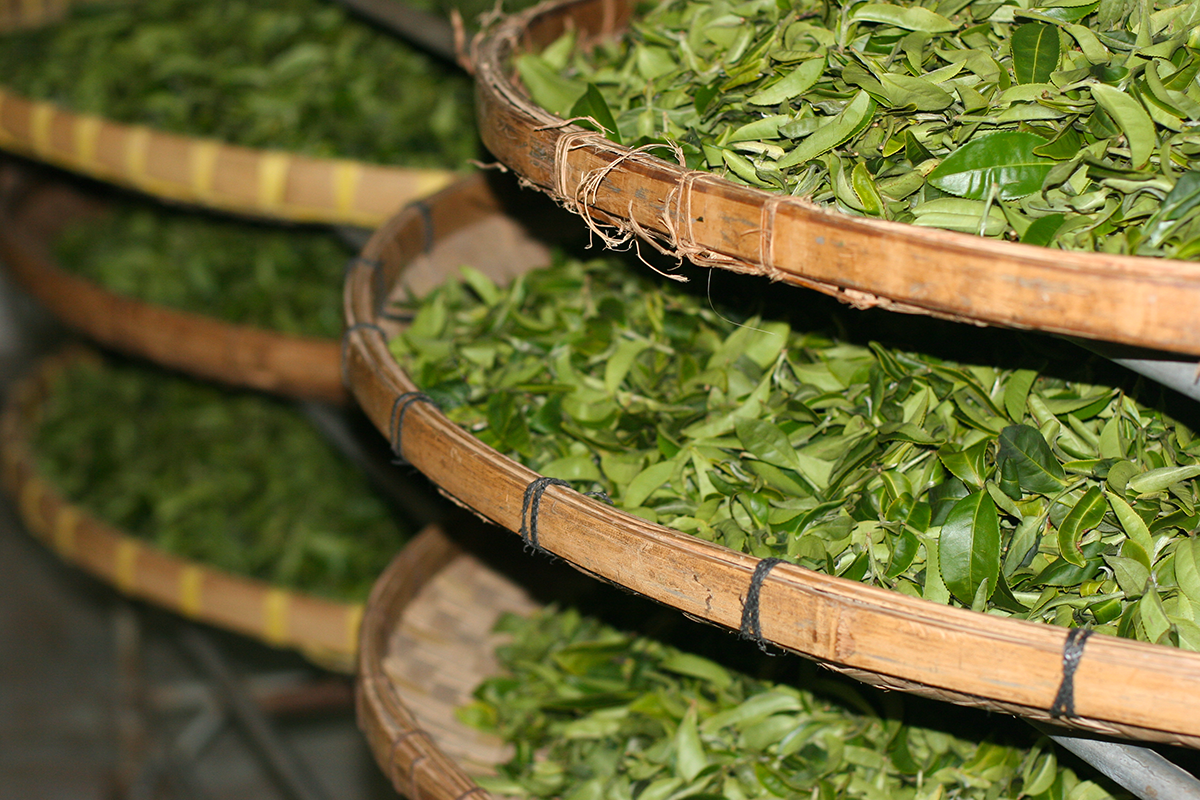
Smoked tea, or Lapsang Souchong, is a speciality of Fujian. It is not very popular with Chinese people, and so it is exported. European food safety regulations were tightened a few years ago, and it is now very difficult to find a smoked tea that meets those standards. This is not due to specific pesticides, but because of a molecule called anthraquinone that forms naturally during the smoking process. For several years I’ve been encouraging a number of farmers to modify their smoking technique so that their tea can be approved. This is a slow, ongoing process, but there have been some positive results.
Tea processing
A wet shirt
Lotus tea is a Vietnamese tradition. To grow the flowers, you have to get wet. You get wet when it’s time to harvest the flowers. You get wet in the pond, either wading through the chest-height water or in the little leaky boats. And you get wet when it’s time to divide up Nelumbo nucifera by plunging your hand down towards the bottom and grabbing a few rhizomes, which will be planted out in another pond.
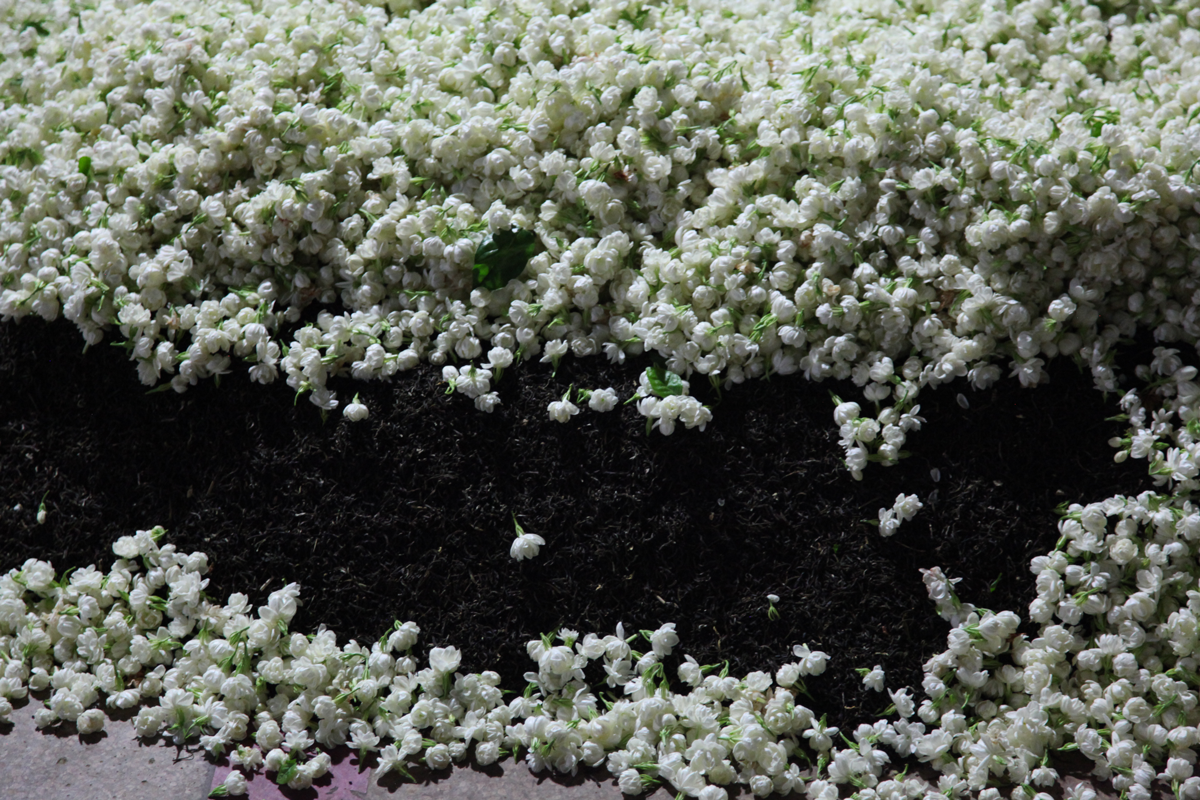
Lotus tea: a Vietnamese tradition
The lotus flower plays a very important role in Vietnamese culture. So it’s not surprising that the country has a tradition of flavouring tea with the flower, resulting in a particularly sought-after beverage. Production takes place in June and July and requires patience, as the tea leaves are left in contact with the flower pollen for five days in a row.
Chinese machines launched the Nepalese revival
Nepal has been producing tea for nearly two centuries. Originally, the culture and organisation of its plantations were based on the model that existed in Darjeeling. But since then, things have evolved considerably. Just over 10 years ago, a number of enthusiastic tea producers wanted to see how things were being done elsewhere, and brought back from Taiwan and China various small-capacity machines that offer a different and much more artisanal solution for processing tea. Today, these machines are widely used in most of the country’s tea co-operatives. Thanks to their introduction and the dedication of the people who use them, we can now enjoy all sorts of teas from Nepal: white, semi-oxidised, shaped into balls… And from a tasting perspective, they are of a remarkable quality.
This revival of Nepalese tea that we’ve seen in the last decade stems from a break with the old British system.
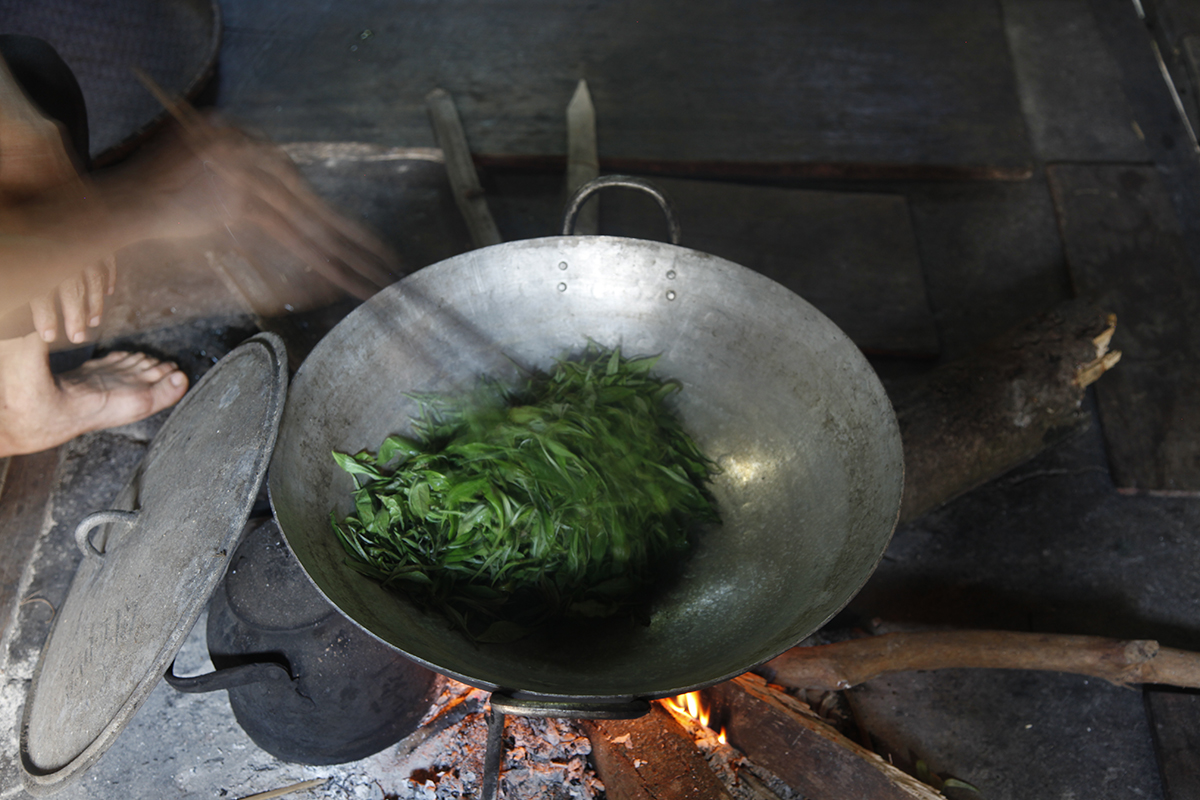
Time to sweat
Black teas are oxidised; green teas aren’t: that’s the difference. With oolongs, it’s more complicated. They can be oxidised a little, a lot, or zealously. Their oxidation rate can range from 10% to 70%. Of course, a lightly oxidised oolong will have a more vegetal aroma, while a more oxidised oolong will develop woody, fruity notes. Whatever the level of oxidation required, the processing steps are the same: withering, sweating, roasting, rolling, then drying. The sweating stage is essential. It involves alternating periods of stirring the leaves with periods of resting them, as illustrated by this photo. The aim of this stage is to encourage oxidation while removing the natural moisture from the leaves.
The art of making jasmine tea
The world’s finest jasmine teas are produced in August and September in Fujian province (China). They are made using a green tea base, and as the best green teas are harvested in April, the necessary quantity is reserved at the time. The jasmine flowers on the other hand, are picked at the end of summer. Jasmine flowers open in the evening, when they release their fragrance. When this happens, they are placed in layers with the tea leaves, impregnating them with their heady scent. Throughout the night they are mixed together to ensure the leaves have absorbed as much of the fragrance as possible. When day breaks they are separated, before the jasmine flowers turn bitter.
A very simple tea
Many types of tea are produced using a specific method or cultivar, or on a defined terroir. While most of these teas are made on modestly sized smallholdings, they are sometimes processed on larger premises with bigger facilities, and even in factories that make tea on an industrial scale. The key difference with teas processed traditionally as opposed to industrially manufactured teas is the artisanal quality of the former; this involves skilled work done by hand, and the process is judged through the feel, appearance and smell of the leaves at every stage.
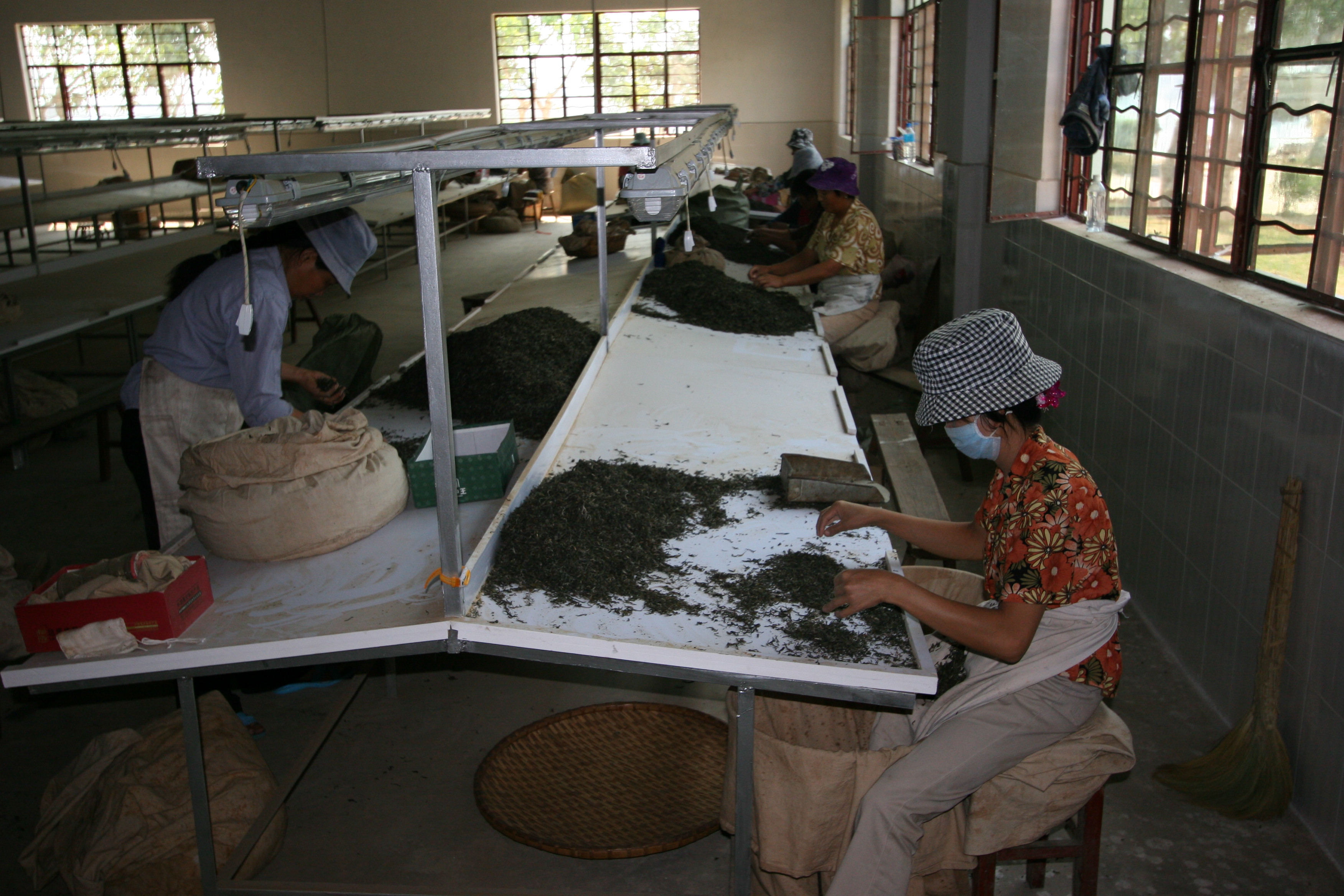
Meticulous work and high standards
It takes a lot of manual work to produce a high-quality tea, except in Japan, where they have designed incredibly sophisticated machines.
Tea leaves are sorted one by one, like here, in China. This is done for any tea worthy of the name; in other words, whole-leaf, good quality tea. This leaf-by-leaf sorting eliminates tiny pieces of stem, as well as any coarser leaves. It is also an opportunity to remove the occasional insect: tea plantations are living environments, and the presence of weeds and insects can be a sign of good farming practice.
A terrible machine for tea
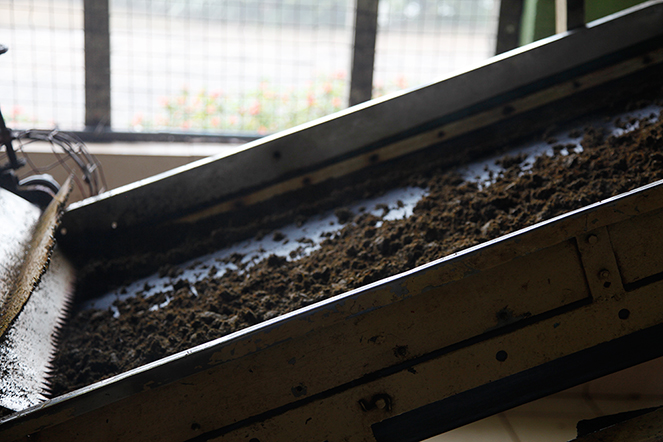
It is difficult to find good tea in Sri Lanka, and here is a photo of the guilty party. Known as a rotorvane, it puts the leaves under enormous pressure and can roll three times the quantity of freshly withered leaves as a traditional roller. The oxidation time can then be reduced to a few minutes because the leaves have been squashed so much.
This procedure is widely used in the mountains in the centre of the country. It has the advantage of increasing yield, but what is the point when you gain strength in lieu of any subtlety of flavour and aroma.