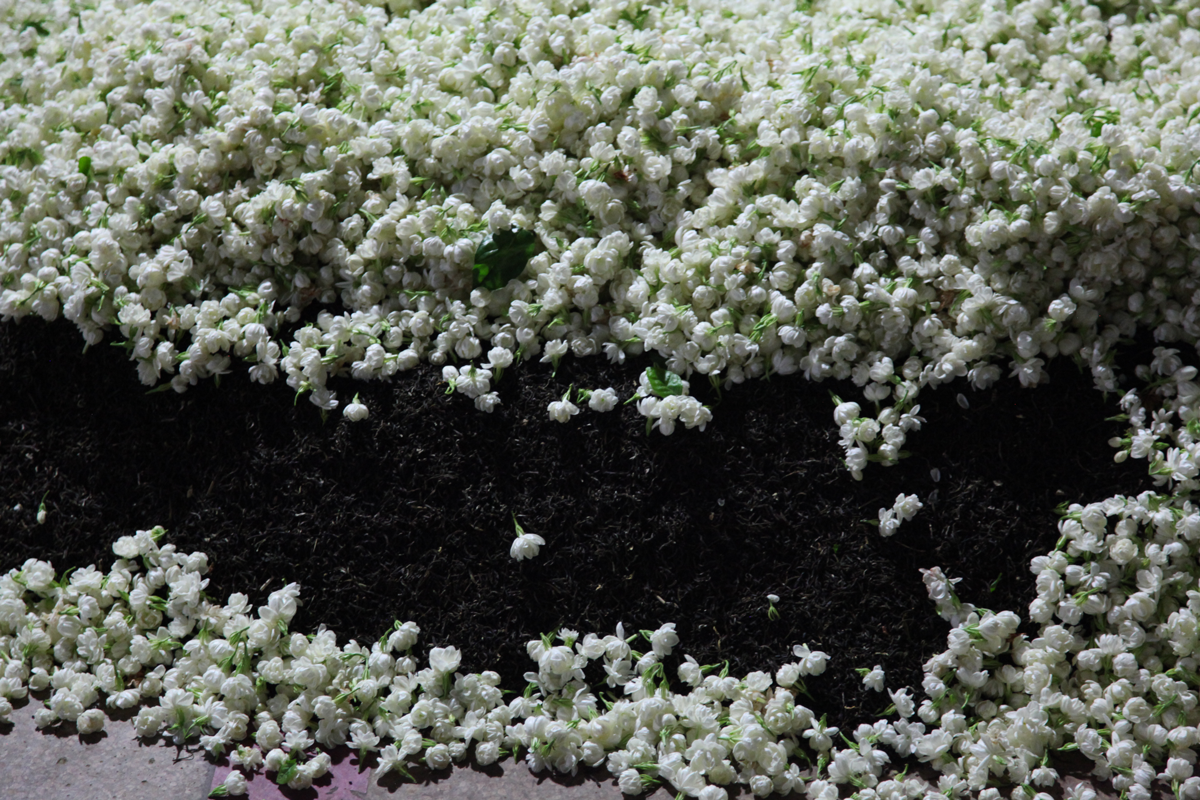
The world’s finest jasmine teas are produced in August and September in Fujian province (China). They are made using a green tea base, and as the best green teas are harvested in April, the necessary quantity is reserved at the time. The jasmine flowers on the other hand, are picked at the end of summer. Jasmine flowers open in the evening, when they release their fragrance. When this happens, they are placed in layers with the tea leaves, impregnating them with their heady scent. Throughout the night they are mixed together to ensure the leaves have absorbed as much of the fragrance as possible. When day breaks they are separated, before the jasmine flowers turn bitter.
From plant to cup
In favour of fair pay
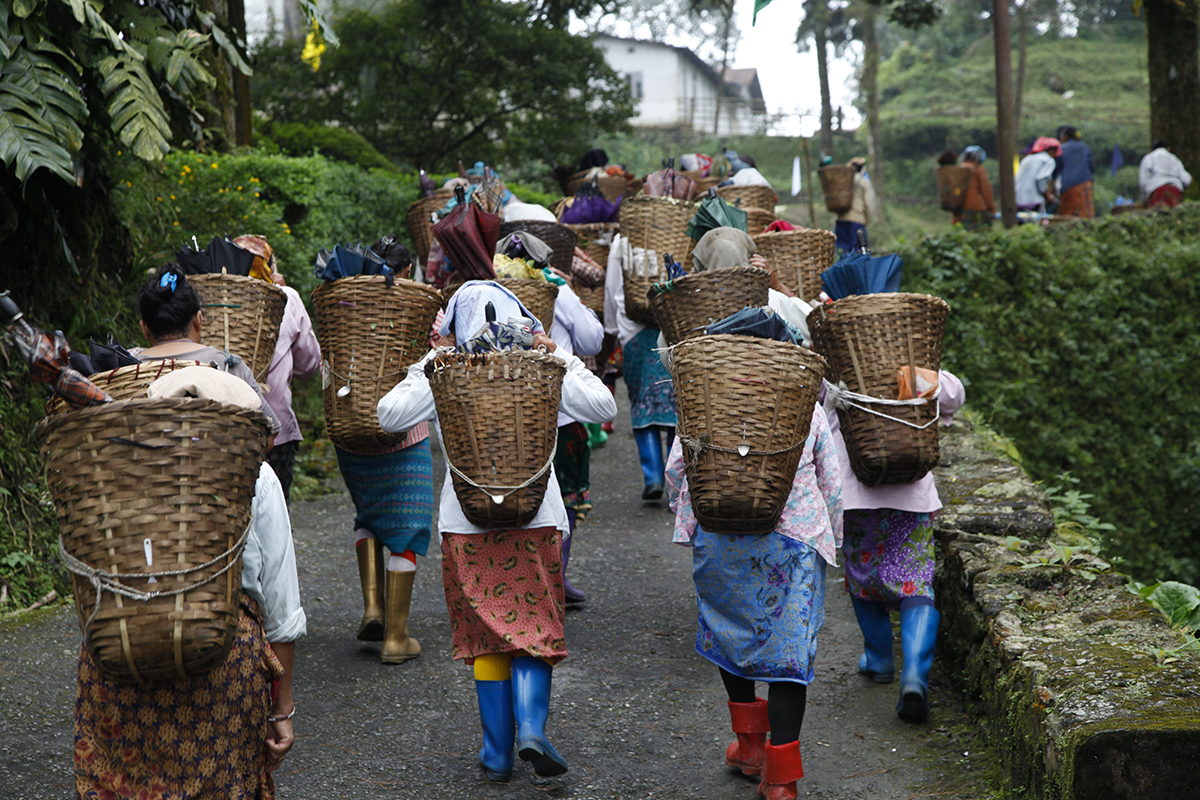
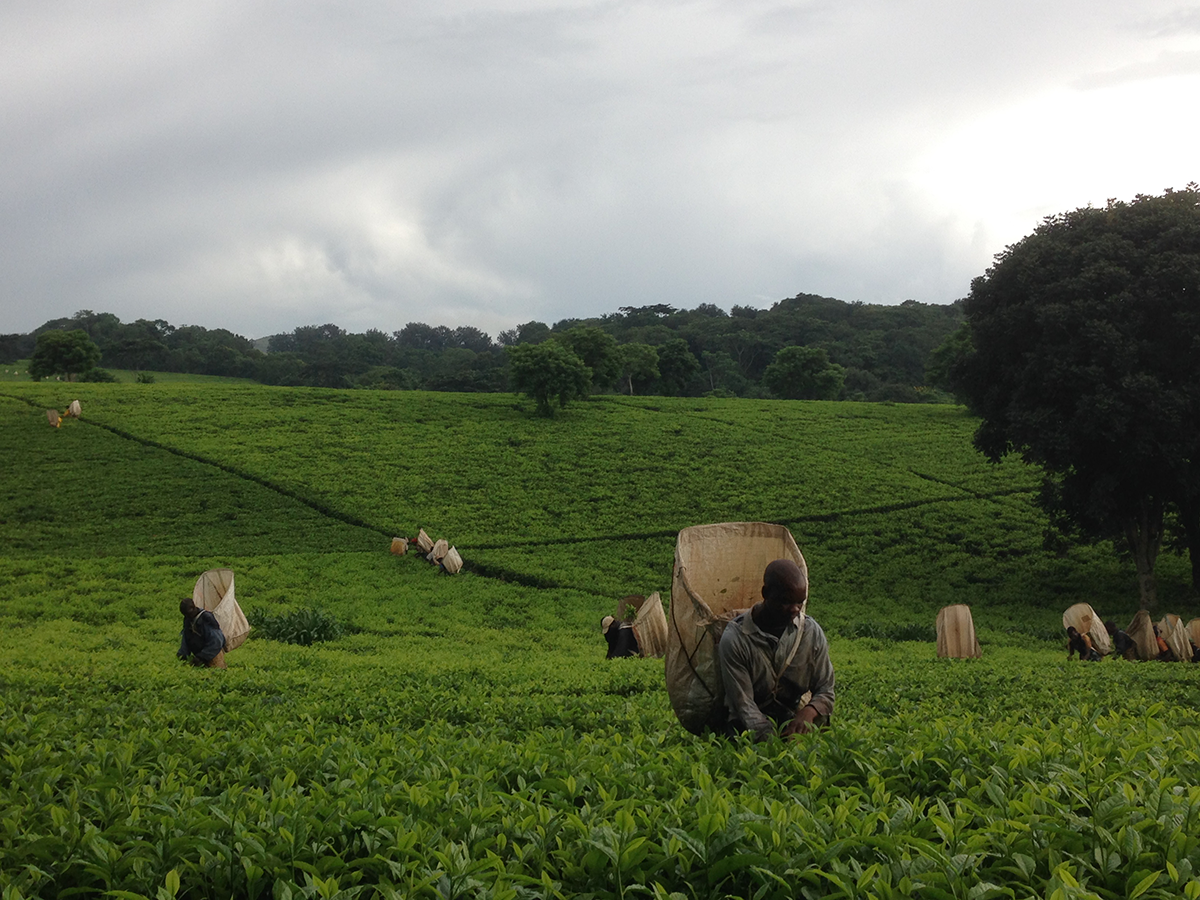
How much longer will tea be harvested by hand in India, where there is ongoing conflict over employment conditions? The pickers are demanding justified pay rises, but the plantations are only just profitable, while some are even loss-making. Tea is already sold at a high price without the benefit being passed on to local populations. Do we risk seeing mechanical harvesting replace manual picking due to a lack of workers? And what will be the consequences on quality? Or are we moving towards plantations being turned into cooperatives so that everyone has a stake in them and can live decently on their wages? These questions have not yet been answered.
Limited production
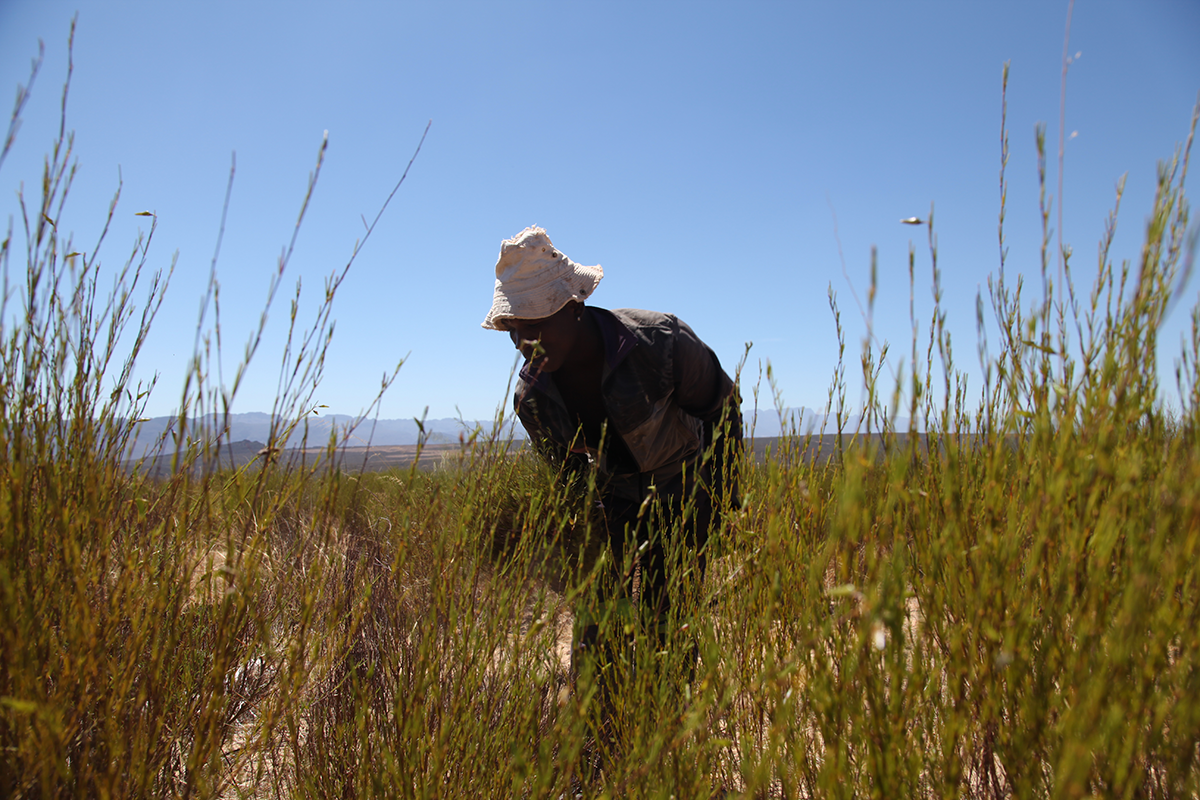
In South Africa, the only country that produces Rooibos, 350 farmers grow it as a crop. Australia and California (United States) tried to grow Rooibos, but failed.
Rooibos is harvested when temperatures are high, by workers who often come from neighbouring countries.
Rooibos, a recent crop
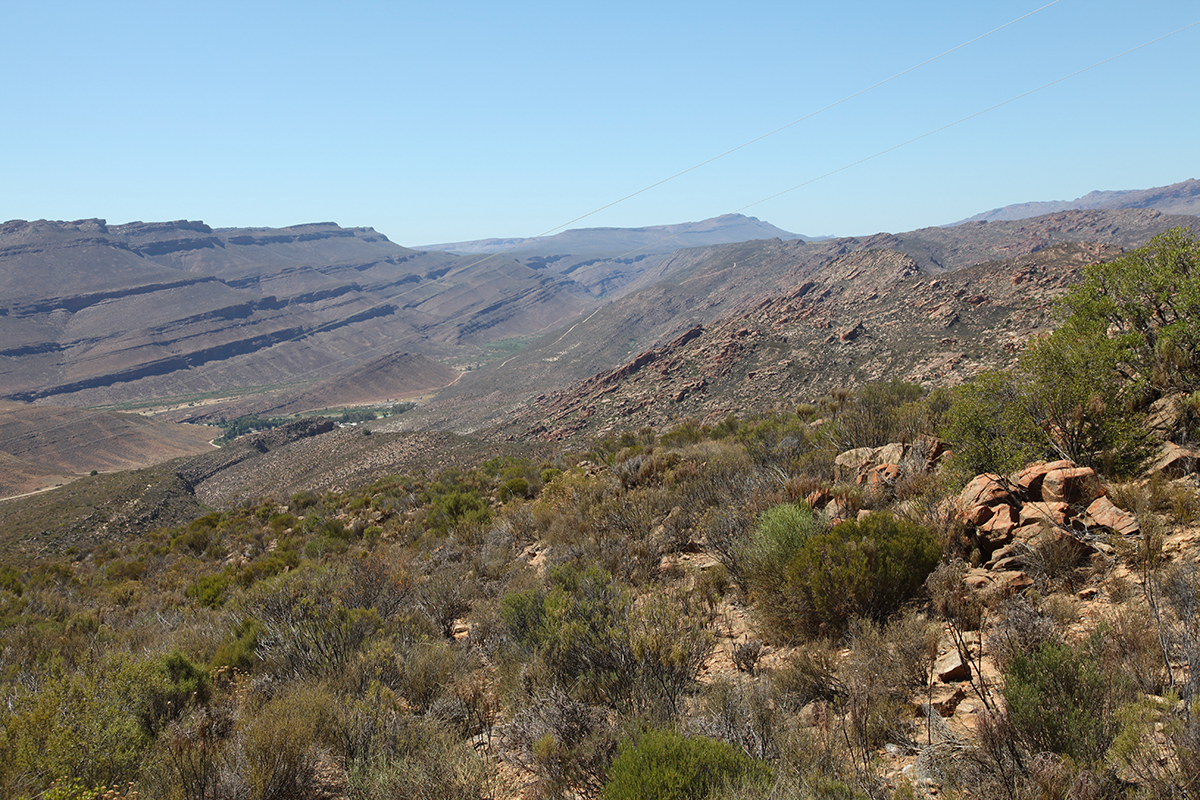
Although rooibos has been consumed for centuries, it has only been grown in recent times. In the mid-19th century, a German priest from Namibia founded the village of Wupperthal in South Africa. He imposed strict rules on the community and set about organising the cultivation of rooibos. Halfway between the Cape and Namibia, Wupperthal is in the middle of the desert. Rooibos, or Aspalathus lineari, is about as undemanding as a camel, and can withstand extreme heat without complaint. The plant’s roots push deep into the ground, which helps it find nourishment. Wupperthal is worth a visit. It’s a journey of several hours along a difficult track, which nonetheless offers some beautiful views for those who like their landscapes arid.
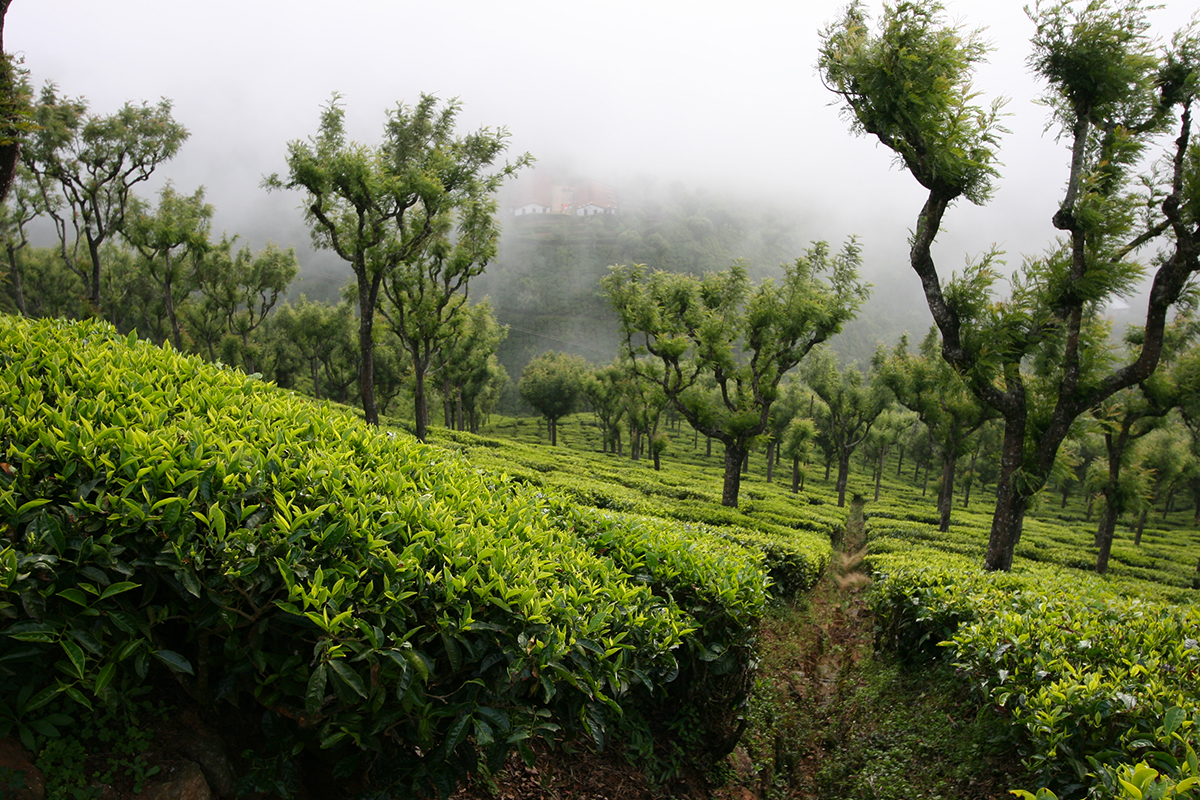
A refreshing mist
Tea plants are like you. In hot weather, they appreciate a refreshing mist. The tea plant belongs to the Camellia family. These plants like water, as long as it doesn’t sit around their roots. This means that tea plants feel at home on sloping ground, preferably in mountainous regions with a warm, humid climate. On flat ground, they require drainage.
Teas worth seeking out
Africa produces enormous quantities of tea – did you know that Kenya is the world’s biggest exporter? It’s mainly low grade, destined for the production of tea bags. But if you look carefully, you can find some incredible teas in countries such as Kenya, Rwanda, Uganda and Malawi. Discovering rare teas in Africa, Asia and elsewhere is what my job is all about. It’s a job that is constantly changing from one season to the next, one year to the next. No two harvests are the same. You must taste again and again, season after season, to find the best teas of the moment.
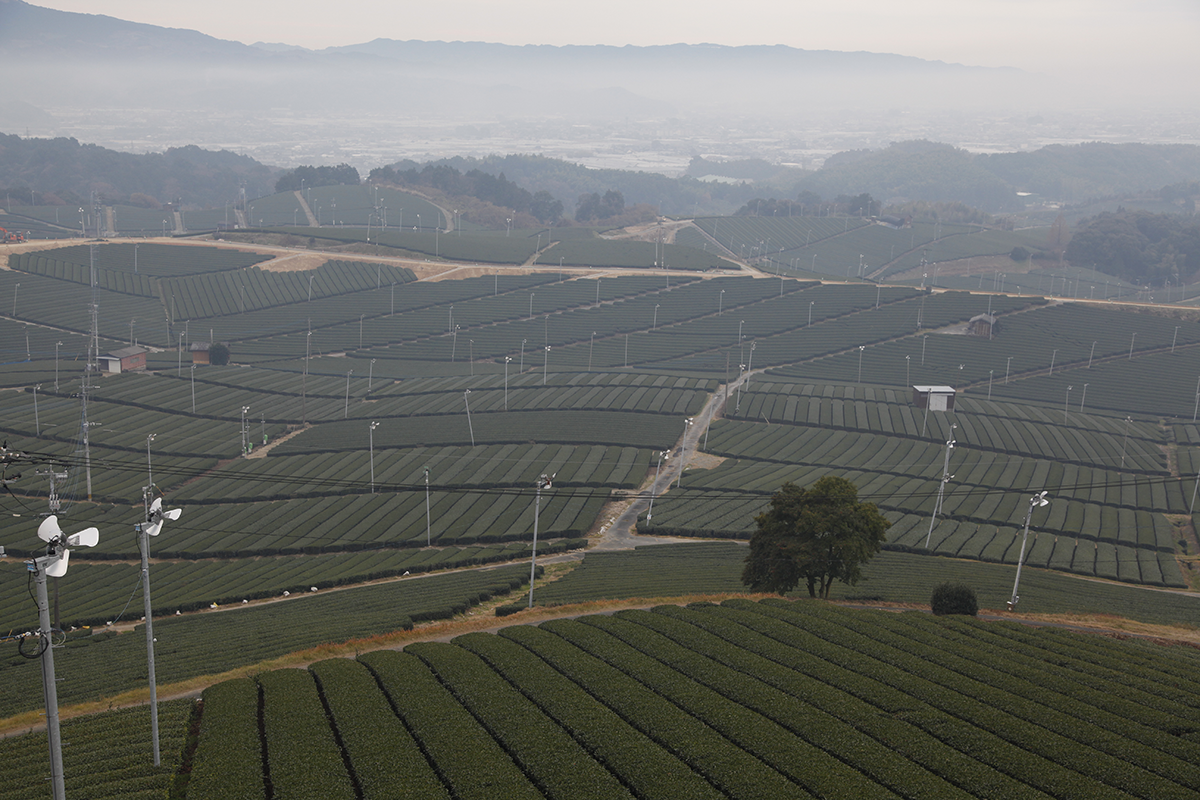
High-precision mechanical harvesting
In most tea-producing countries, tea leaves are harvested by hand. Japan is an exception, the main reason being the high cost of manpower. However, the sophisticated machinery used by Japanese farmers allows them to be very precise when harvesting. Only the young shoots are picked, which are then sorted with the most rigorous standards, in the factory, using machines with electronic eyes.
The first harvest is the best
Since the start of May, I’ve been tasting and choosing the best teas of the season from Japan. They’re called Ichibanchas because they’re the first to be harvested in the year. Japanese teas come from the regions of Shizuoka and Uji, and in the south of the archipelago. In the north of the country, the tea plant grown everywhere is Yabukita, whereas in the south, with its warmer climate, less Yabukita is grown. For example, here, near Kagoshima, the Yutaka Midori cultivar dominates, and represents nearly 60% of production.
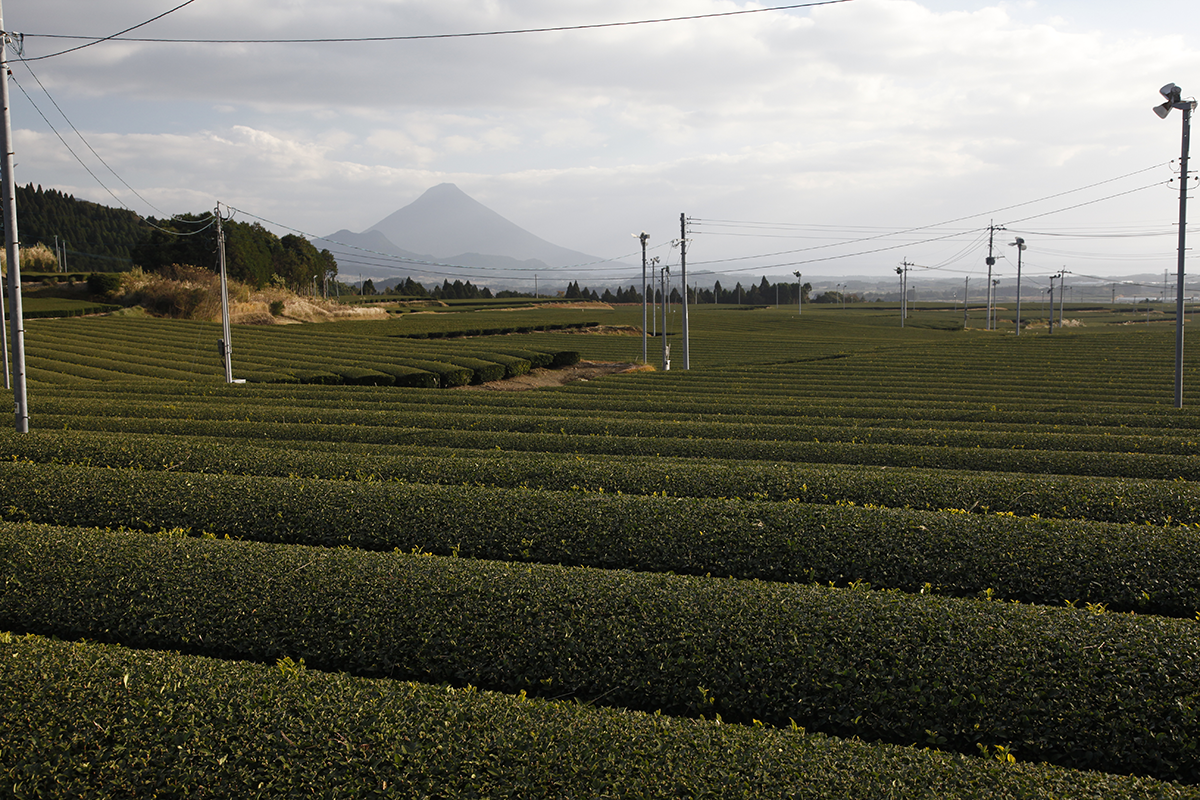
A volcano in the landscape
On the island of Kyushu in Japan, it isn’t unusual to find a volcano in your field of vision. As someone who enjoys photography, this makes me very happy. The outline of these lava giants emphasises the controlled horizontality of the tea plants. They disrupt a rather too orderly landscape. They also remind us that the duration of harvests, the duration of seasons, the duration of human life, quite simply, is infinitesimal. Here is Mount Kaimon, which has a silhouette similar to that of Mont Fuji.
An unusual season
The Darjeeling season is going to be a strange one. The really amazing teas are priced out of reach (30% to 50% higher than in previous years) to compensate, the planters say, for the losses they sustained during the 105 days of strikes last year. So far I’ve bought, on the best possible terms, the following: Mission Hill DJ4 SFTGFOP1 Clonal, Puttabong DJ14 SFTGFOP1 Clonal Exotic, Puttabong DJ12 SFTGFOP1 Clonal Queen, Orange Valley DJ5 SFTGFOP1 cultivar China, Balasun DJ6 SFTGFOP1 Himalayan Mystic, and Rohini DJ15 FTGFOP1 Exotic White, all exclusive. They’re of a remarkable quality and will delight enthusiasts. For those wanting first-flush Darjeelings at lower prices, you’ll have to wait. Firstly, the only teas that are cheap are very poor quality, and secondly, even the mediocre teas are priced high, or very high. They’re absolutely not worth it. To sum up, this year requires more vigilance than usual.
For fans of Himalayan teas who aren’t focused on Darjeeling, and who are looking for good deals, why not wait for the Nepalese teas? They’ll be ready soon and often represent excellent value for money.