Lotus tea is a Vietnamese tradition. To grow the flowers, you have to get wet. You get wet when it’s time to harvest the flowers. You get wet in the pond, either wading through the chest-height water or in the little leaky boats. And you get wet when it’s time to divide up Nelumbo nucifera by plunging your hand down towards the bottom and grabbing a few rhizomes, which will be planted out in another pond.
From plant to cup
Lotus tea: a Vietnamese tradition
The lotus flower plays a very important role in Vietnamese culture. So it’s not surprising that the country has a tradition of flavouring tea with the flower, resulting in a particularly sought-after beverage. Production takes place in June and July and requires patience, as the tea leaves are left in contact with the flower pollen for five days in a row.
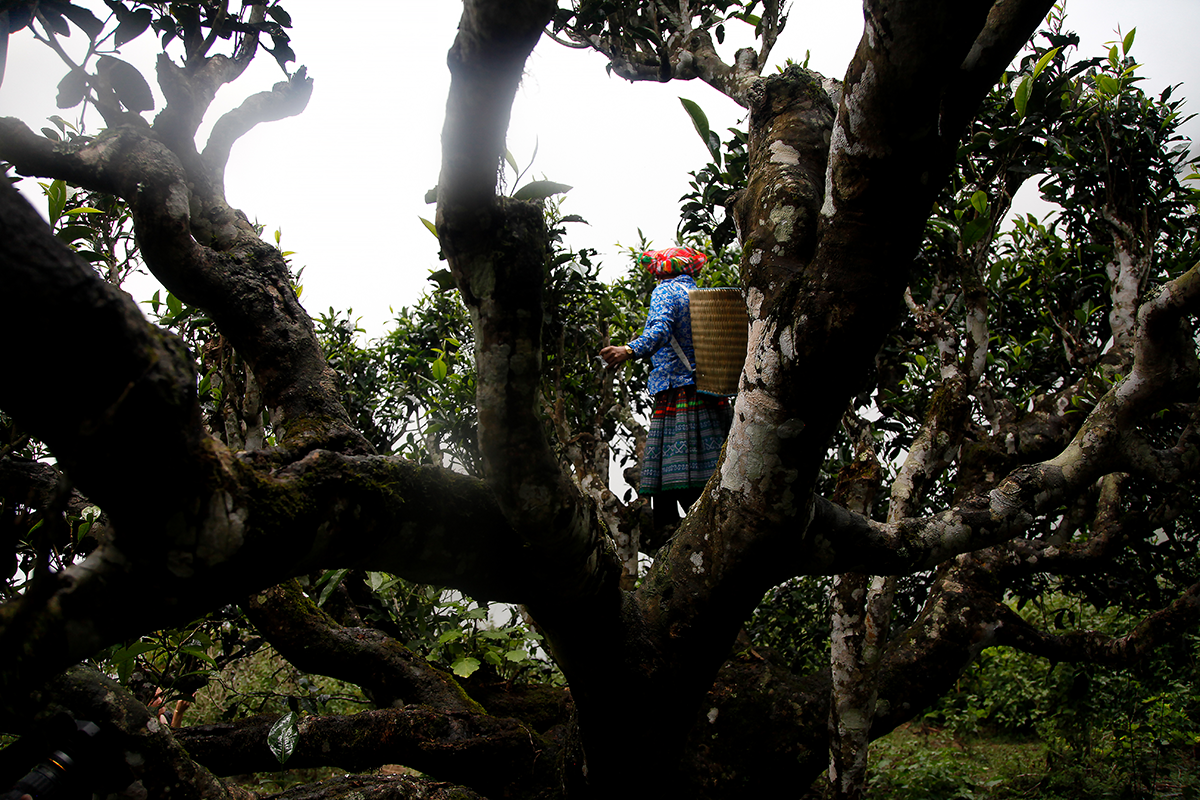
Harvesting in the treetops in the Golden Triangle!
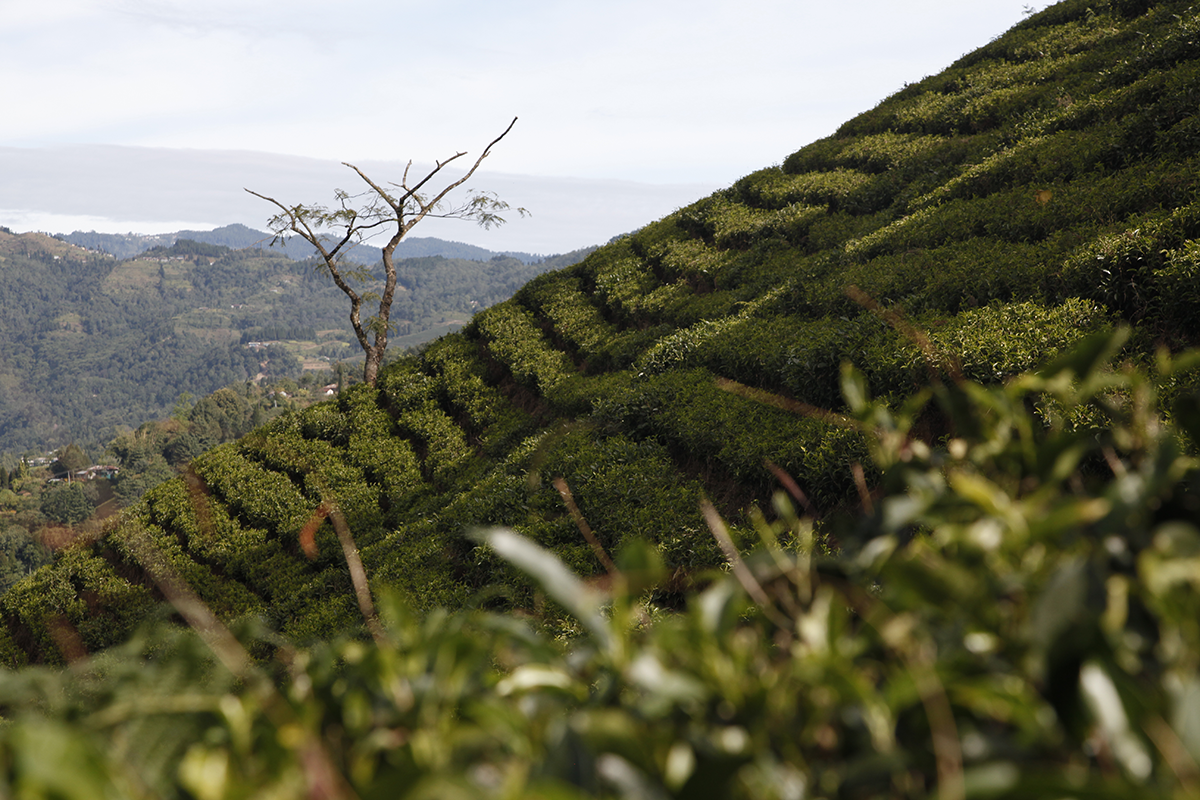
In the region known as the Golden Triangle, you can find tea plants that are not quite like the others. Instead of being pruned at a low level to make it easier to pick the leaves, they are left to grow like trees. When harvest time comes, the pickers must climb up into the camellias, some of which are several hundred years old. The leaves from these trees are particularly sought-after to make Pu Erhs and dark teas.
Chinese machines launched the Nepalese revival
Nepal has been producing tea for nearly two centuries. Originally, the culture and organisation of its plantations were based on the model that existed in Darjeeling. But since then, things have evolved considerably. Just over 10 years ago, a number of enthusiastic tea producers wanted to see how things were being done elsewhere, and brought back from Taiwan and China various small-capacity machines that offer a different and much more artisanal solution for processing tea. Today, these machines are widely used in most of the country’s tea co-operatives. Thanks to their introduction and the dedication of the people who use them, we can now enjoy all sorts of teas from Nepal: white, semi-oxidised, shaped into balls… And from a tasting perspective, they are of a remarkable quality.
This revival of Nepalese tea that we’ve seen in the last decade stems from a break with the old British system.
You can’t rely on a name, even a prestigious one
Tea can be complicated in that you cannot rely on a name as a gauge of quality, for the simple reason that tea grows in regions which often experience significant variations in weather. This results in variations in quality. One example is that during the monsoon, it rains non-stop for weeks on end, and the tea is obviously not good. A prestigious plantation that sometimes produces remarkable teas in the best seasons is not capable of doing the same during the rainy months. So a prestigious garden can also produce bad teas. This means it’s important for a tea researcher like myself to taste every tea before buying, and never rely on a name. And it’s also important for the customer to be well informed and guided by skilled sales advisers.
An inaccurate French name
The first Darjeelings of the year are generally described as the “first flush” in English, but in French, they’re known as the “spring harvest”. The latter is misleading as the harvest doesn’t fully coincide with the season. There are two reasons for this. Firstly, the low-altitude plantations that use irrigation techniques benefit from more clement weather and sometimes start producing small batches from the end of February. Secondly, the leaves on the same shoots are harvested every eight to ten days, and after three successive growths, the shoot’s thwarted growth leads it to send out a side shoot (this is known as the banjhi), which is of a lower quality and marks the end of the first harvests. This means that the so-called “spring harvests” actually come to an end around mid-April.
Safe passage
I’ve finished selecting my first-flush Darjeelings – 12 premium teas in total. From Puttabong to Thurbo, Namring Upper and Highlands, they represent the best of what these mountains have produced during the season. Now I want to tell you about the steps that follow the purchase of a tea of exceptional quality. First, the tea is packaged up on the plantation itself, then transported by truck to the nearest airport. From there, it travels to Paris, and on to the Palais des Thés warehouses. A sample of the batch is then sent to the lab for analysis. Once we’ve received confirmation of its compliance with the Safetea standards that are the pride of Palais des Thés, it is distributed to our various stores. The journey from plantation to cup takes several weeks and cannot be rushed. It’s a mark of quality and safety.
Are you more Clonal Superb or China Exotic?
Indians use the name inherited from the British to describe tea leaves (see my previous blog post). However, in the past few years, they haven’t been content with the letters “FTGFOP” or even “SFTGFOP1”. So they’ve added more words, generally nice ones. Some have a specific meaning. Others sound pretty, and the producer uses them to indicate that this exceptional tea is worth an exceptional price, for the highest bidder.
The former include the words China, Clonal and AV2, which refer to the tea plant. They stand for a variety that comes from China (Camelia sinensis sinensis), a hybrid (the word clonal is therefore inappropriate in French), and the specific name of the variety (AV2 for Ambari Vegetative no. 2), respectively.
As for the latter, the imagination is the only limit when it comes to such terms as Exclusive, Delight, Exotic, Superb, Mystic and more. There’s also Wonder, Enigma and Euphoria. I bet that in the next year or two I’ll be offered Nirvana!
Darjeeling Opens the Season
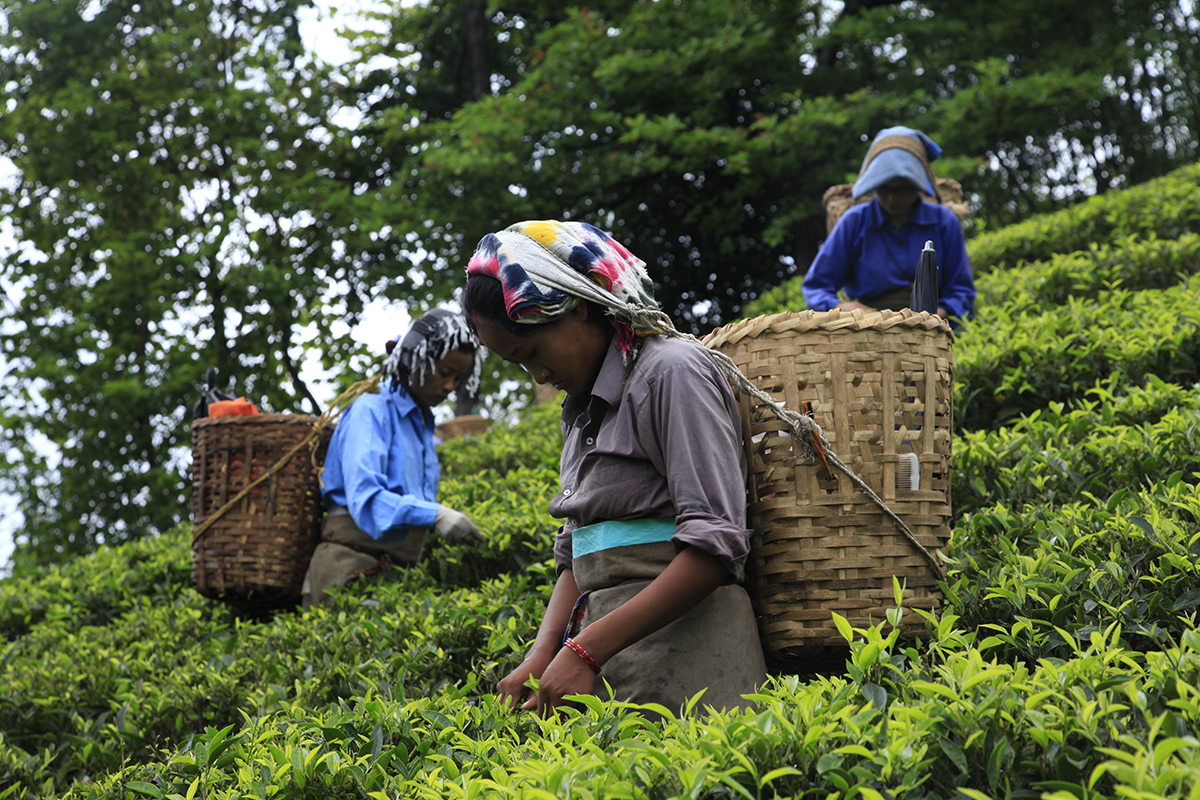
First flush teas are often the best, as the year’s first harvest. With winter coming to a close, cold nights keep the plants growing slowly, which results in richer flavours. Every year, it is Darjeeling that opens the season, before Nepal, China, or Japan.
In March, I sometimes taste nearly a hundred teas a day, with each of the 87 tea estates in Darjeeling manufacturing very small batches—sometimes no more than 20 or 30 kilos. In this region, during the period when the highest quality of tea is produced, one day’s harvest is never mixed with the next. The result is a constant parade of very different tastings. Buyers snap up the very best batches in a matter of hours, at premium prices, which is why it is so important to know every producer and maintain the best possible relationship with each of them.
Tell me about tea!
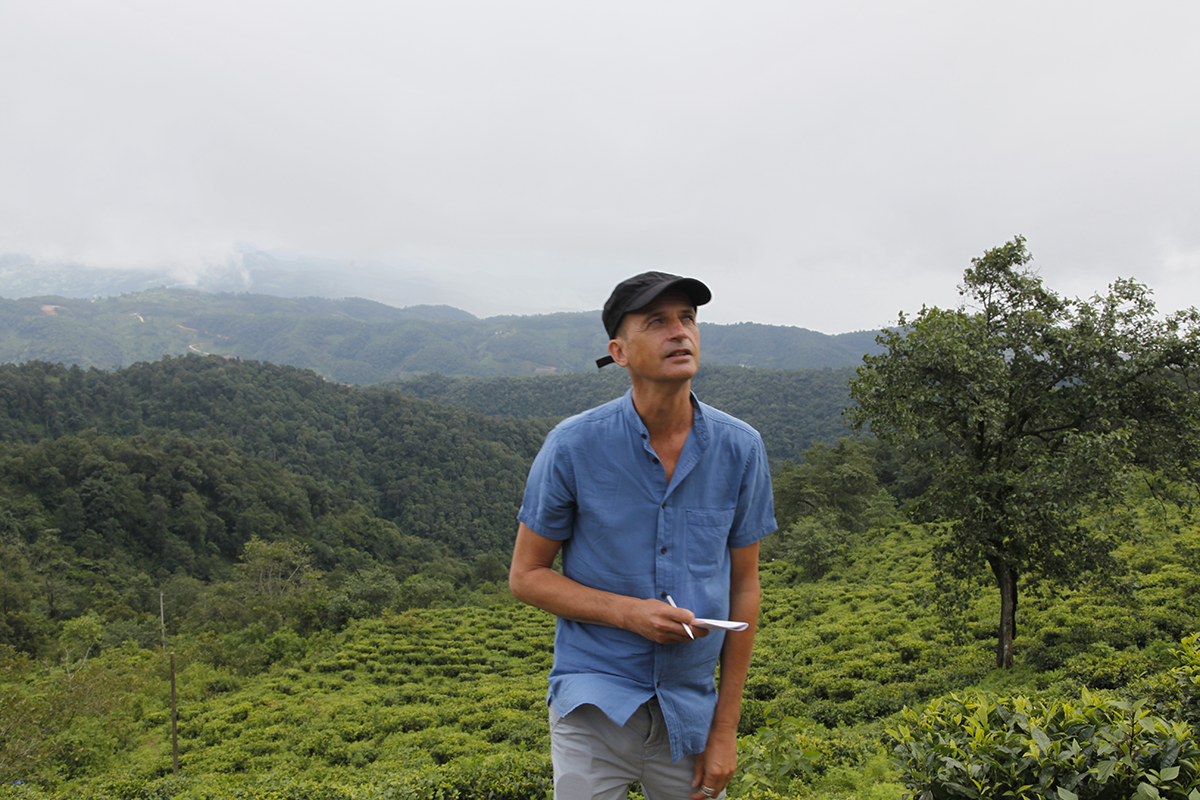
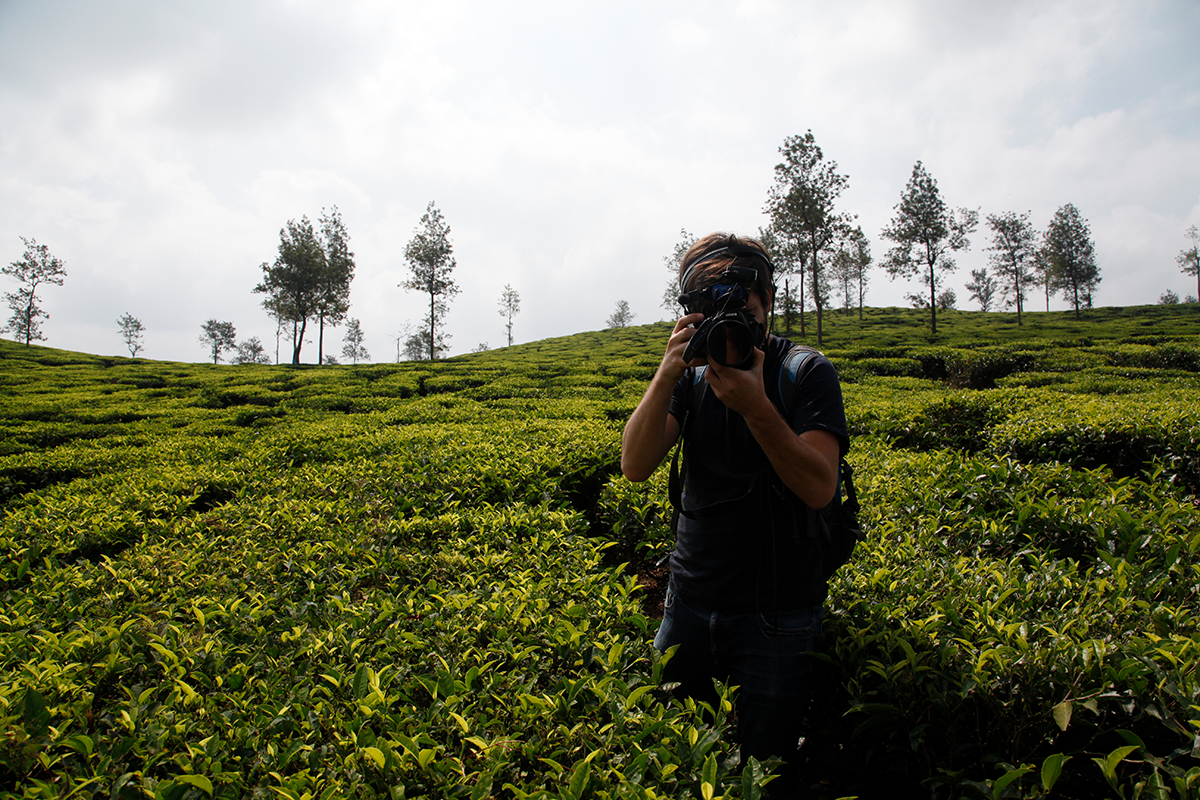
On tea plantations, I come across pickers, of course, as well as villagers walking home. More rarely, I also come across television crews. I’ve just spent two days with Julie and Romain, who asked to join me. Julie is a journalist and Romain, pictured here, is a television reporter. They wanted me to talk about my work, and also to carry on as if they weren’t there, so that they could observe me in the tea fields, tasting tea and talking to people I meet. With them in tow, my work is a bit different from usual, but just as interesting. As with customers who come into a shop for the first time and ask “Tell me about tea!”, I explain as much as I can to them – about life on the plantation and how to make the best teas. Now I’m looking forward to seeing their wonderful report, which will be broadcasted on 16 March at 7 p.m during the programme “50 Minutes Inside” on the French television channel TF1. I think it will only last a few minutes – the time it takes to have a cup of tea.